Importance of asset leasing in the manufacturing industry
In the capital-intensive manufacturing sector, asset leasing is not merely a financing alternative, it is a strategic enabler of operational efficiency, financial flexibility, and technological advancement. With manufacturing companies facing increasing pressure to optimize costs, modernize equipment, and scale operations globally, leasing has emerged as a critical tool for sustaining competitive advantage while maintaining financial agility. Let’s explore the key benefits of asset leasing in the manufacturing industry.
Preserving capital for core business growth
Manufacturers must balance capital expenditures between acquiring production assets and funding core business initiatives, such as research and development, supply chain optimization, and market expansion. Leasing enables manufacturers to access high-cost assets such as industrial machinery, robotics, and transportation fleets, without significant upfront investment.
For example, an automotive manufacturer may lease robotic welding systems for an assembly line rather than purchasing them outright. This approach preserves working capital, allowing the company to allocate resources toward innovations in electric vehicle production rather than being locked into depreciating fixed assets.

Enhancing technological competitiveness with continuous equipment upgrades
Manufacturing is a rapidly evolving industry where obsolescence is a constant challenge. Emerging technologies such as IoT-enabled smart factories, AI-driven predictive maintenance, and automated material handling systems, are reshaping production processes. Purchasing such equipment outright can result in outdated assets within a few years, creating inefficiencies and lowering competitiveness.
By leveraging leasing, manufacturers can continuously upgrade to the latest-generation equipment, ensuring that production lines remain optimized without the financial burden of disposing of outdated assets. This is particularly advantageous in high-tech sectors, such as semiconductor manufacturing, where cutting-edge equipment is required to maintain precision and efficiency.
Scaling production capacity with operational flexibility
Leasing allows manufacturers to scale production capacity in response to market demand without committing to long-term capital investments. This flexibility is crucial in industries with fluctuating demand cycles, such as consumer electronics, automotive, and food processing.
For instance, a packaging manufacturer experiencing seasonal spikes in demand may lease additional production lines for six months rather than investing in permanent equipment that may sit idle during off-peak periods. This strategic use of leasing reduces financial risk while ensuring production remains agile.

Mitigating risk through maintenance and service contracts
One of the most overlooked advantages of leasing is the ability to transfer certain operational risks to the lessor. Many lease agreements include full-service maintenance contracts, ensuring that leased machinery remains in optimal condition without burdening the manufacturer with unexpected repair costs.
For example, an aerospace components manufacturer leasing CNC (computer numerical control) machining centers may negotiate a lease that includes predictive maintenance analytics, reducing downtime and preventing costly production halts. By outsourcing maintenance to the lessor, manufacturers can focus on operational efficiency while avoiding capital-intensive repair expenses.
Navigating regulatory and environmental compliance requirements
Governments worldwide are tightening regulations around energy consumption, emissions, and workplace safety in industrial operations. Leasing provides manufacturers with an adaptable approach to complying with evolving regulations without incurring significant capital expenditures.
For instance, an industrial steel manufacturer facing stricter emissions laws may opt to lease energy-efficient smelting furnaces equipped with carbon capture technology rather than committing to a full-scale investment in new infrastructure. This approach allows manufacturers to remain compliant while maintaining financial flexibility to adapt to future regulatory changes.
Facilitating global expansion and supply chain resilience
Manufacturers operating across multiple regions must manage a complex network of production facilities, distribution centers, and logistics hubs. Leasing plays a key role in enabling global expansion by allowing companies to establish new facilities and acquire necessary assets without significant upfront costs.
For example, a multinational electronics manufacturer entering a new market may lease production facilities and warehouse space rather than investing in owned real estate. This strategy provides the flexibility to scale operations based on demand, reducing exposure to geopolitical and economic uncertainties.
Types of leased assets in manufacturing
Manufacturers rely on a vast range of assets to keep operations running smoothly. From production machinery to logistics fleets, leasing provides a way to access critical equipment without the heavy financial burden of outright ownership. Let’s break down the key types of leased assets in manufacturing and why they matter.

Production equipment and machinery
Manufacturing is all about efficiency, and the right machinery is at the heart of that. Instead of buying expensive equipment that might become obsolete in a few years, manufacturers often lease:
- CNC machines: These machines are fundamental in industries like aerospace and automotive, where precision cutting and shaping are essential. Leasing these machines allows manufacturers to access high-tech, specialized equipment without the financial risk of ownership. With leasing, manufacturers can upgrade to newer models as technology advances, ensuring they always have access to the latest capabilities without having to deal with the depreciation costs of ownership.
- Injection molding machines: Used in plastic component manufacturing, these machines are crucial for creating high volumes of identical parts. Leasing allows companies to meet production demands without overcommitting capital to machinery that might become outdated or over-specified as production volumes change.
- 3D printers and additive manufacturing systems: Increasingly popular in prototyping and custom manufacturing, 3D printing allows manufacturers to produce complex parts on demand. Leasing gives companies the flexibility to experiment with new processes and scale production quickly without the upfront investment.
- Automated assembly lines: In industries like consumer electronics or automotive manufacturing, automated assembly lines are essential for high-volume production. Leasing such systems helps manufacturers avoid the high upfront costs associated with setting up these intricate, often highly specialized systems. Moreover, it allows for quick upgrades to incorporate new technologies that can improve production speed and reduce errors.
Leasing production equipment not only reduces upfront costs but also allows manufacturers to upgrade to newer, more efficient models without the risk of getting stuck with outdated technology.

Material handling and warehousing equipment
Efficient material flow is key in manufacturing, whether it’s moving raw materials into production or storing finished goods. Leasing options for material handling equipment include:
- Forklifts and pallet jacks: Essential for moving goods within warehouses and production floors, these pieces of equipment help manufacturers streamline internal logistics. Leasing these assets provides flexibility, ensuring that companies can scale their material handling capabilities up or down based on production needs without having to invest heavily in ownership and maintenance.
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs): Used in modern, smart factories for internal logistics, AGVs are essential for automating the movement of materials across production facilities. Leasing AGVs helps manufacturers take advantage of cutting-edge automation technology without the financial strain of purchasing these high-cost systems.
- Conveyor belt systems: Conveyor systems are vital for automating production and packaging lines. By leasing conveyor systems, manufacturers can ensure they have the capacity to meet production requirements while avoiding large upfront costs. This flexibility allows companies to easily expand or reconfigure production lines as market conditions change.
- Storage racking and shelving systems: These systems are needed to maximize space in warehouses and production areas, particularly in high-density storage environments. Leasing allows manufacturers to adjust their warehousing capabilities quickly, particularly when demand fluctuates or when new inventory needs to be stored.
Leasing material handling equipment allows manufacturers to scale up when demand increases without over-investing in assets that might not be fully utilized year-round.
Transportation and logistics assets
Manufacturers need a reliable supply chain to move raw materials, distribute products, and keep operations running efficiently. Rather than owning fleets that require heavy maintenance and depreciate quickly, manufacturers often lease:
- Trucks and trailers: Used for moving goods between production facilities, warehouses, and customers, trucks and trailers are crucial for maintaining a seamless logistics operation. Leasing these vehicles helps manufacturers avoid the burden of maintaining a fleet while still ensuring they have the necessary transportation capacity to meet demand.
- Railcars and shipping containers: For global manufacturers, railcars and shipping containers are essential for moving materials across long distances. Leasing these assets allows companies to expand their logistical reach without the capital investment and upkeep required by owning a fleet.
- Delivery vehicles: For companies that handle their own distribution, leasing delivery vehicles ensures that they can scale their fleet to meet changing demand, without worrying about maintenance costs or depreciation.
By leasing transportation assets, manufacturers avoid the financial burden of maintenance, insurance, and fleet management, allowing them to focus on production and delivery efficiency.

Manufacturing facilities and real estate
Manufacturing companies often lease physical space, whether it’s for production, warehousing, or corporate offices. Key leased assets include:
- Factory space: Instead of building new plants, companies lease industrial facilities to adapt to market demand. This flexibility allows manufacturers to scale their operations up or down based on order volumes or market changes. It also provides a cost-effective alternative to owning real estate, especially in regions with high property costs.
- Warehouse and distribution centers: Leasing warehouse space is common for companies managing large volumes of goods. As manufacturers grow or shift operations, leasing ensures they don’t get locked into long-term commitments that might not align with future business needs.
- Office buildings and R&D labs: As manufacturers expand into new markets or enhance their research capabilities, leasing office space or R&D facilities provides flexibility without long-term commitment. Manufacturers can adjust the size of their facilities as necessary, especially when entering new regions or shifting operational strategies.
- Build-to-suit Facilities: For manufacturers with very specific facility requirements, build-to-suit leases are a popular choice. In this arrangement, a developer constructs a facility tailored to the manufacturer’s precise specifications, whether it’s for specialized production processes, advanced storage needs, or specific regulatory compliance requirements. This type of lease offers the customization of ownership without the financial burden of building or owning a facility, providing manufacturers with the perfect fit for their operational needs.
Leasing real estate gives manufacturers the agility to expand or downsize based on economic conditions, without the capital-intensive commitment to buying property.
Specialized equipment for compliance and sustainability
Manufacturing companies face increasing pressure to meet environmental and safety regulations. Instead of investing in expensive upgrades, many lease:
- Energy-efficient HVAC and air filtration systems: To comply with workplace safety and environmental standards, manufacturers may need to invest in systems that control air quality or reduce energy consumption. Leasing these systems allows manufacturers to remain compliant without making a huge upfront investment.
- Industrial wastewater treatment systems: For industries like chemical or food manufacturing, wastewater treatment is essential to meet environmental standards. Leasing this equipment ensures that manufacturers can maintain compliance with local regulations without committing to expensive infrastructure.
- Renewable energy solutions (e.g., solar panels, battery storage): As sustainability becomes a priority for many manufacturers, leasing renewable energy solutions allows them to reduce energy costs and meet their sustainability goals without the upfront capital costs associated with purchasing and installing these systems.
Leasing these assets allows companies to stay compliant with evolving regulations without major upfront costs.
Discover our buyer’s guide with RFP scorecard designed to simplify the selection of lease accounting solutions for the manufacturing industry. With tailored evaluation criteria and practical insights, this guide helps you navigate the decision-making process and identify the tools best suited to your organization’s unique needs.
How lease accounting software solves complex challenges for global manufacturers in each step of the lease lifecycle

Challenge 1: Large, global, and multi-faceted manufacturing portfolio
Managing leases in a large, global manufacturing environment presents a unique set of challenges. Manufacturers often deal with complex, multi-faceted lease portfolios that span multiple regions, asset types, currencies, and regulatory landscapes. These challenges require sophisticated solutions to ensure efficiency, compliance, and financial accuracy. Below are some of the key challenges global manufacturers face in lease accounting:
- Mass lease management across multiple locations: Manufacturers with operations in multiple regions or facilities face significant difficulties in managing the vast number of leases across these diverse locations. Each facility might have its own set of lease agreements, varying lease terms, renewal conditions, and compliance requirements. This complexity is further compounded by the need to track long-term leases for machinery and equipment, office space, warehouse properties, and other assets. Managing leases at this scale often leads to inefficiencies and a lack of visibility across the entire lease portfolio.
- Multi-currency management: Global manufacturers frequently enter into leases denominated in foreign currencies, depending on the jurisdiction of the leased asset. This creates added complexity in lease accounting, particularly with the need for precise currency translation and remeasurement in accordance with standards like IAS 21 and ASC 830. Exchange rate fluctuations can have a significant impact on the valuation of lease liabilities, right-of-use (ROU) assets, and related expenses when translated into the functional or presentation currency. Mishandling exchange rates can lead to discrepancies in consolidated financial statements, complicate audits, and pose compliance risks with both local and international regulations. The challenge becomes even greater for long-term leases, where accumulated currency movements over time can materially affect the organization’s balance sheet and overall financial performance.
- Multi-calendar management: Manufacturers operating in multiple countries must navigate different fiscal years and business calendars. This diversity creates complications in tracking lease terms, managing renewals, and ensuring timely financial reporting. Different fiscal calendars also make it difficult to align lease liabilities, ROU assets, and expenses across the organization. Without a unified calendar structure, it can be hard to maintain consistent and accurate financial records across global operations. This inconsistency can lead to confusion when preparing consolidated financial statements and makes it more difficult to ensure that lease-related expenses, liabilities, and ROU assets are accurately reflected in the correct reporting periods.
- Multi-contract structures: In the manufacturing sector, lease agreements often vary significantly based on the type and use of the asset. While some may involve long-term commitments for production equipment, others cover short-term needs like office space or vehicle fleets. Manufacturers frequently engage in complex, multi-contract arrangements that differ by jurisdiction and applicable accounting standard. For instance, under ASC 842, a single contract may contain both operating and finance lease components, whereas IFRS 16 generally classifies all leases as finance leases. Accurately tracking and managing these variations demands a flexible and robust lease accounting solution. Many contracts also include renewal options, purchase clauses, or rent escalations tied to inflation or market indices, all of which require careful monitoring. These structural differences introduce significant complexity, making it challenging to maintain accurate records and ensure full compliance with evolving regulatory requirements.
- Complex analytics requirements: In a global manufacturing context, extracting actionable insights from lease data is both essential and complex. The scale and diversity of lease portfolios across asset classes, geographies, and currencies demand advanced analytics capabilities. Yet, many organizations face fragmented data sources and limited reporting tools, hindering visibility into lease performance, liability forecasting, and compliance tracking. Addressing this challenge requires integrated solutions that not only consolidate data but also deliver real-time, strategic insights to support informed decision-making at every level of the organization.
How Nakisa solves large, global, and multi-faceted manufacturing portfolio challenges
Nakisa Lease Accounting offers a suite of features specifically designed to support the scale, complexity, and regulatory requirements of global manufacturing organizations. These capabilities address the operational and financial challenges manufacturers face when managing diverse lease portfolios that span regions, currencies, asset types, and business units.
- Multi-currency capabilities: For global manufacturers operating across multiple countries, managing leases in a variety of currencies is critical. Nakisa Lease Accounting provides advanced multi-currency support that enables manufacturers to process lease payments and perform calculations in local contract currencies, while maintaining compliance and consistency in functional and reporting currencies. This is especially useful for manufacturers managing plants, equipment, or logistics leases in jurisdictions with volatile exchange rates. The system automatically handles currency revaluation and translation adjustments in accordance with IAS 21 and ASC 830, minimizing the risk of discrepancies in consolidated financial reporting.
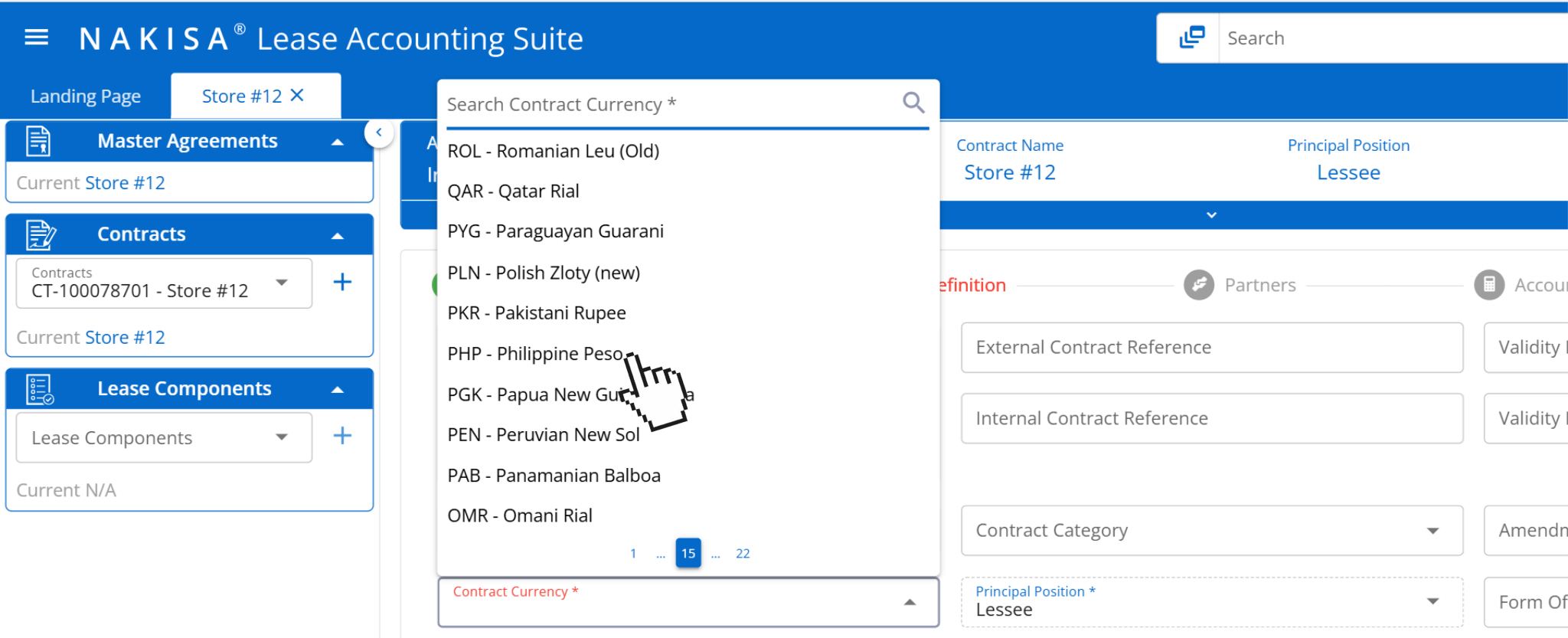
In Nakisa Lease Accounting software, users can apply any type of contract currency to support global lease portfolios.
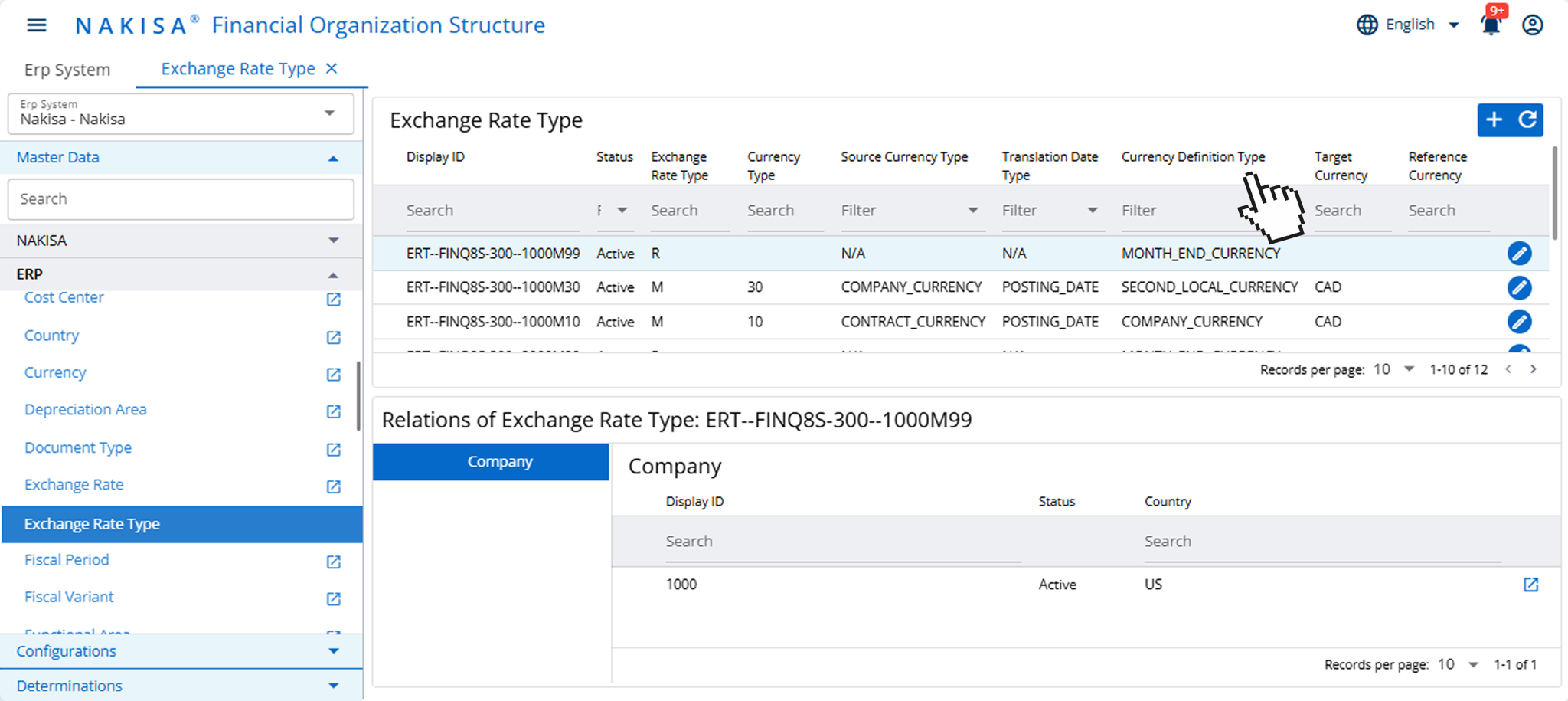
In Nakisa’s Financial Organization Structure, users can define information related to the exchange rate type.
- Mass operations, automation, reversal, and detailed logs: With thousands of leased assets ranging from specialized equipment to global warehousing space, manufacturers require high-efficiency tools for lease management. Nakisa’s mass operation capabilities enable bulk data uploads, validations, and automated event processing. Lease administrators and accountants can modify terms, trigger remeasurements, and adjust ROU assets across entire portfolios without manual intervention. Bulk integrations with ERP systems facilitate automated postings of journal entries, depreciation, and asset lifecycle events, reducing the operational burden on accounting teams. Additionally, reversal tools allow manufacturers to retroactively adjust leases due to changes in contract terms, audit findings, or accounting policy shifts. All actions are fully logged, providing a transparent audit trail and real-time tracking for internal controls and external auditors.
Interactive demo: Mass indexation
- Contract tracking and management: Manufacturing leases often involve layered contracts, such as master equipment agreements, site-level head leases, subleases, and bundled service components (e.g., facility maintenance, utility contracts, technical support). Nakisa Lease Accounting allows users to manage multiple contracts under a single master lease structure, with the ability to assign, categorize, and monitor each component. For example, a production facility lease may include embedded leases for forklifts, HVAC systems, and power generators. Nakisa enables finance and operations teams to track each element’s lease terms, payment schedules, and renewal conditions, centralizing visibility and ensuring that all related liabilities and disclosures are captured accurately.
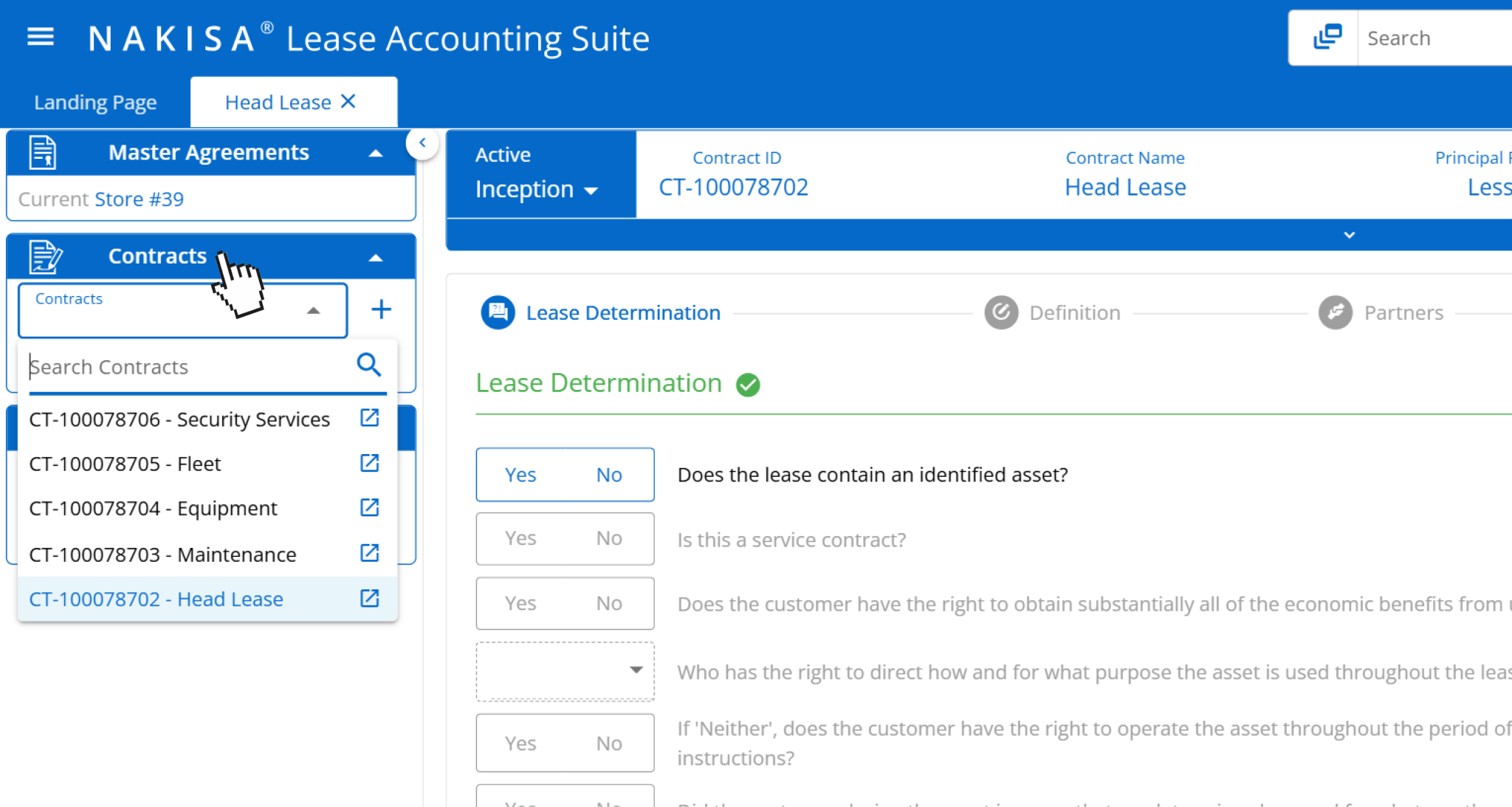
In Nakisa Lease Accounting software, users can track and manage multiple contracts under the same master lease agreement.
- Multi-calendar support: Enterprise manufacturers often operate in jurisdictions with varying fiscal calendars such as 4-4-5 structures in North America or standard calendar years in Europe or Asia. Nakisa Lease Accounting supports multiple calendar types, including regular calendar, 360-day convention, and configurable fiscal variants. This flexibility allows lease accounting activities and reporting to align with local entity financial periods, while still supporting centralized consolidation and reporting at the group level.
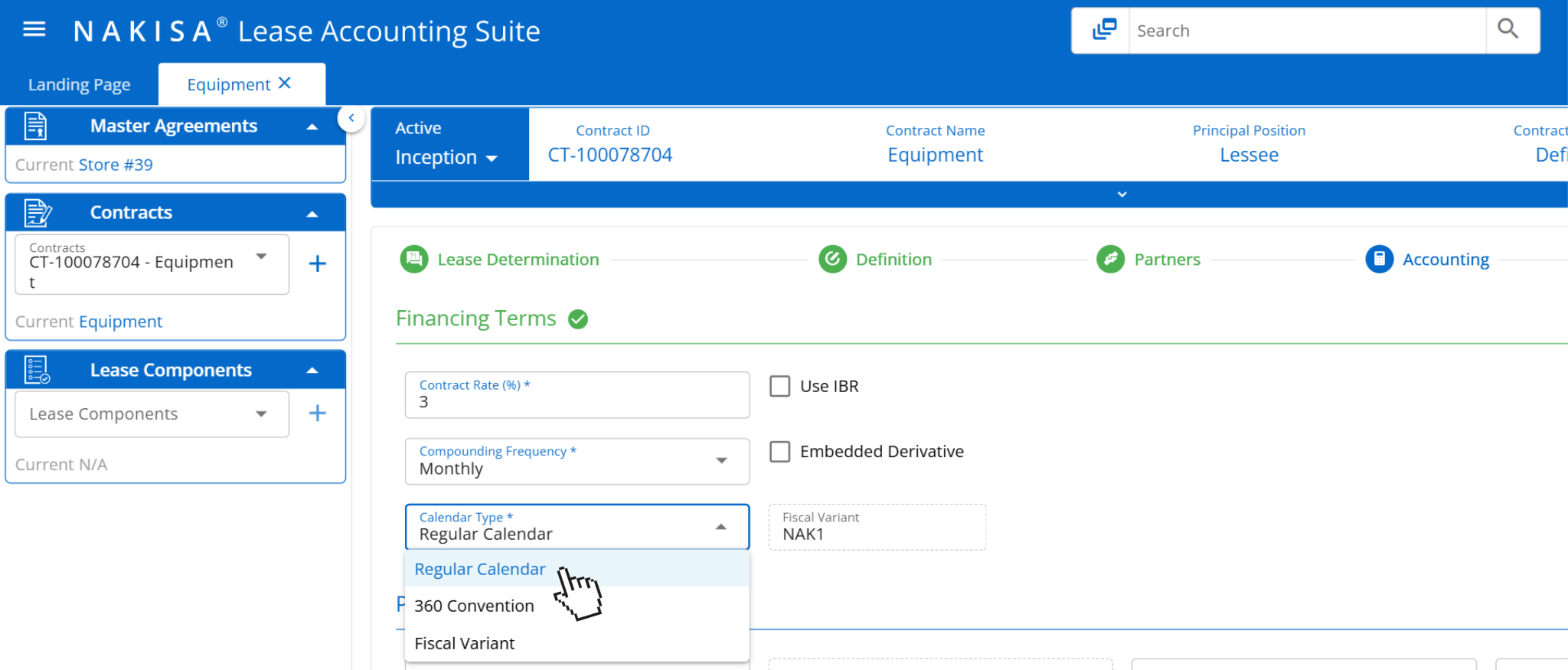
Nakisa Lease Accounting software supports various calendar types such as regular calendar, 360 convention, and fiscal variant.
- Multi-language support: Manufacturers typically run cross-border operations with finance teams, plant managers, and legal departments working in different countries and languages. Nakisa’s multi-language interface allows global users to interact with the system in their preferred language, reducing miscommunication and enhancing accuracy during contract review, lease data entry, and reporting processes. This supports smoother global adoption, localized compliance, and improved collaboration across multinational teams.
- AI-powered analytics: Nakisa Lease Accounting elevates analytics through intuitive, real-time dashboards that transform complex lease data into strategic insights. These customizable dashboards empower users to visualize key performance indicators (KPIs) and track portfolio trends across multiple dimensions, such as asset types, locations, and currencies. Whether at the company or individual user level, the dashboards are designed to provide tailored views that support precise decision-making with no-code formulas and flexible scripting. The Nakisa AI Agent further enhances analytics by automating data analysis and delivering AI-powered insights directly within the dashboard. By intelligently assessing available datasets, the AI Agent automatically surfaces insights through charts, metrics, and key indicators. This enables users to quickly identify trends and make data-driven decisions, significantly reducing the time and effort spent on manual data analysis. With this advanced capability, teams can extract value from complex datasets with speed and precision, empowering them to act on insights faster and more effectively.


Olof Ruhe
Product Owner, Tax and Statutory Reporting at Volvo Car
Case study: Nestlé’s global lease accounting transformation with Nakisa Lease Accounting
Before adopting Nakisa Lease Accounting (NLA), Nestlé needed to transition a vast and complex lease portfolio to the cloud without impacting business continuity. The project required a solution that could support global operations, ensure IFRS 16 compliance, integrate seamlessly with SAP, and meet rigorous cybersecurity standards. Here are some key details that illustrate the scope of their lease management needs:
- Company revenue: $94B USD
- Number of contracts: 40,000 with 70,000 monthly journal entries across 360 company codes
- Types of assets: Real estate and equipment
- ERP systems: Multiple SAP systems
- Employees: 352,000 across 360 companies in 189 countries
After implementing Nakisa Lease Accounting, Nestlé successfully migrated its data to the cloud using Nakisa’s lift-and-shift strategy. The solution provided strong integration with multiple SAP systems, ensuring granular financial visibility and smooth data flow. The cloud migration was completed with no major issues, enabling Nestlé to achieve compliance, improve operational efficiency, and enhance security while future-proofing its lease management system.
Dana Jircikova
Head of Capital and Financial Investments Reporting at Nestlé’s Corporate Financial Reporting Team

Challenge 2: Complex fixed and variable rent calculations in manufacturing leases
In manufacturing, lease agreements rarely follow a standard pattern. Instead, they’re often shaped by industry-specific operational demands, from output fluctuations to resource consumption. These complex arrangements create significant challenges when it comes to compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842, especially around the classification, measurement, and recognition of lease liabilities and right-of-use (ROU) assets. Manufacturers must deal with varying rent structures, non-linear escalations, and conditions that are highly sensitive to external or internal performance triggers. All of this adds complexity not only to lease calculations, but also to ensuring accurate and compliant financial disclosures across global portfolios. Let’s explore key challenges faced by manufacturers.
Output-based or productivity-linked rent payment challenges
In the manufacturing sector, certain leases, such as those for specialized equipment or machinery, often include rent components that vary based on operational metrics like machine uptime, units produced, or production volumes. For example, a manufacturer leasing CNC machinery might pay a base rent plus a variable amount for each machine hour used. While IFRS 16 and ASC 842 exclude variable rent from lease liability calculations, these payments must still be tracked and disclosed in financial reporting. Accurately managing and reporting these variable components becomes essential for compliance and scaling operations. Here are some of the key challenges manufacturers face:
- Complex rent structures tied to operational metrics: Leases may include base rent plus a variable component based on machine hours, units produced, or uptime, requiring precise tracking and separation from fixed lease components.
- Compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842: Performance-based rent is excluded from lease liability calculations but must still be disclosed accurately. Misclassification can lead to non-compliance.
- Manual tracking is unsustainable at scale: Manufacturers operating numerous facilities or equipment leases struggle to manage usage-based rent calculations manually, increasing the risk of reporting errors.
- Lack of visibility in financial disclosures: Without a clear system for capturing and reporting variable rent data, disclosures can be incomplete or inconsistent, affecting transparency and audit readiness.
How Nakisa solves output-based or productivity-linked rent payment challenges
While output-based or productivity-linked rent payments present unique accounting challenges, Nakisa Lease Accounting offers flexible tools and capabilities that help manufacturers navigate these complexities. From configuring variable payment structures to ensuring proper disclosure and reporting, Nakisa supports scalable and compliant lease accounting, even for the most operationally dynamic leases. Let’s explore how these features can help streamline the process.
- Customizable lease payment terms: Nakisa Lease Accounting provides flexibility to manage both fixed and variable rent payments within the Payment Term module. For leases with a base rent and productivity-linked payments, users can configure the system to handle different types of payment components. This allows manufacturers to easily track, and report fixed rent, while also accounting for variable components based on operational metrics like machine usage or production output. The system is designed to keep these two components separate, ensuring accurate financial reporting and compliance.
- Dynamic lease recalculation and reporting: For leases with output- or performance-based components, Nakisa enables automated tracking and reporting of variable rent tied to factors such as machine usage or sales. While these variable payments are excluded from lease liability and right-of-use (ROU) asset calculations under IFRS 16 and ASC 842, Nakisa uses pre-configured payment terms to ensure accurate recognition in the P&L. This allows manufacturers to effectively manage complex lease structures, monitor cost impacts, and maintain compliance with accounting standards.
- Comprehensive reporting for compliance and auditing: Nakisa Lease Accounting’s robust reporting features allow manufacturers to generate detailed reports that separately track fixed and variable lease payments. These reports ensure that variable rent payments, although excluded from lease liability calculations, are still disclosed correctly in financial statements. This level of transparency ensures compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 and makes it easier to pass audits.
- Automated remeasurement of lease liabilities: When lease modifications or index-based variable payment changes require remeasurement under IFRS 16 or ASC 842, Nakisa Lease Accounting automatically updates lease liabilities and right-of-use (ROU) assets. The system reflects changes such as revised lease terms, updated CPI indices, or contractual adjustments to future fixed payments, eliminating manual effort and ensuring accurate, compliant lease accounting.
- Seamless integration with operational data: Nakisa Lease Accounting enables manufacturers to achieve end-to-end visibility by integrating seamlessly with operational systems like manufacturing execution systems (MES), ERP platforms, fleet management, and procurement systems through flexible APIs. This interconnected approach ensures that real-time data ranging from machine usage and production volumes to fleet utilization and procurement terms, flows directly into the lease accounting system. As a result, variable lease components, such as rent tied to machine hours or mileage, are automatically updated, while asset acquisitions, maintenance events, and contract modifications are captured accurately. This reduces manual effort, enhances audit readiness, and empowers finance teams with precise, up-to-date lease data aligned with operational realities.
Escalation clauses
While fixed rent structures in manufacturing leases offer a level of predictability, the inclusion of escalation clauses introduces a significant layer of complexity. These clauses are often tied to inflation indices, commodity prices, or operational milestones, and can substantially impact financial planning, budgeting, and compliance. In manufacturing, where leases span warehouses, logistics centers, and specialized production equipment, tracking and accounting for these clauses is critical. Here’s how escalation clauses affect lease management in the manufacturing context:
- Escalation tracking and forecasting: Manufacturing leases frequently include index-based increases, such as adjustments tied to the Consumer Price Index (CPI), Producer Price Index (PPI), or even commodity prices like steel and energy. For example, a lease on a metal processing facility may escalate quarterly based on fluctuations in raw material costs. These index-linked rent adjustments directly impact lease payment schedules and the remeasurement of lease liabilities. Manufacturers must project these changes accurately to ensure proper valuation of both lease liabilities and right-of-use (ROU) assets under IFRS 16 and ASC 842. Failure to align these projections with contractual terms can result in non-compliance or misstated liabilities.
- Varying legal requirements and external factors: For global manufacturers, managing escalation clauses requires navigating country-specific regulations around rent adjustments. Some jurisdictions enforce strict rules on indexation, while others allow flexible negotiation terms. When coupled with currency fluctuations, especially in contracts involving imported machinery, these clauses can become even more complex. Systems need to support localized compliance logic and multi-currency scenarios to correctly apply escalations, mitigate financial risk, and avoid regulatory violations.
- Complexity in lease renewal or termination: Lease renewals or early exits often come with revised escalation clauses. For instance, renewing a 10-year lease on a manufacturing plant might switch from fixed annual increases to CPI-linked or commodity-based adjustments. Additionally, escalation clauses may behave differently upon renewal, some might reset, while others may compound. Each scenario requires accounting teams to reassess and remeasure the lease using updated inputs, ensuring accurate updates to the lease liability and ROU asset. Errors here can lead to audit flags or discrepancies in financial reporting that misrepresent operational costs.
- Impact on financial reporting: Mismanagement of escalation clauses can result in material misstatements across both the balance sheet and income statement. Over- or underestimating future rent payments due to poor modeling of indexation or milestone-based clauses can distort cost projections and impair key financial ratios. This is especially true in leases with multi-tiered escalation clauses where contracts include fixed annual increases, CPI adjustments, and productivity-linked rent hikes, each occurring at different intervals (yearly, bi-annually, or event-driven). Accurate modeling is crucial during both initial measurement and ongoing remeasurement phases. Any misalignment may not only disrupt financial forecasting but also lead to non-compliance during audits.
How Nakisa solves escalation clause challenges for manufacturers
Escalation clauses in manufacturing lease contracts, especially those tied to commodity indices, CPI, or operational milestones, can significantly affect lease valuations and compliance. Nakisa Lease Accounting streamlines the handling of these clauses with automation, visibility, and control:
- Accurate escalation projections: Nakisa’s Payment Term module helps manufacturers manage complex lease terms such as CPI-linked increases, commodity-based escalations, or fixed step-ups. Whether it's a lease on a warehouse or heavy equipment, users can configure escalation schedules to reflect contract-specific terms. Users can automate calculations for future rent increases, dynamically adjusting based on published indices or contractual thresholds. This eliminates manual tracking and ensures both compliance and audit-readiness throughout the lease lifecycle.
Interactive demo: Escalating rent
- Real-time adjustments to liabilities and ROU assets: When escalation clauses result in changes to future fixed or index-based payments such as CPI-driven increases or contractual revisions tied to milestone events, Nakisa Lease Accounting automatically remeasures lease liabilities and right-of-use (ROU) assets. These updates flow directly into financial statements, reducing the risk of delayed reporting and ensuring compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
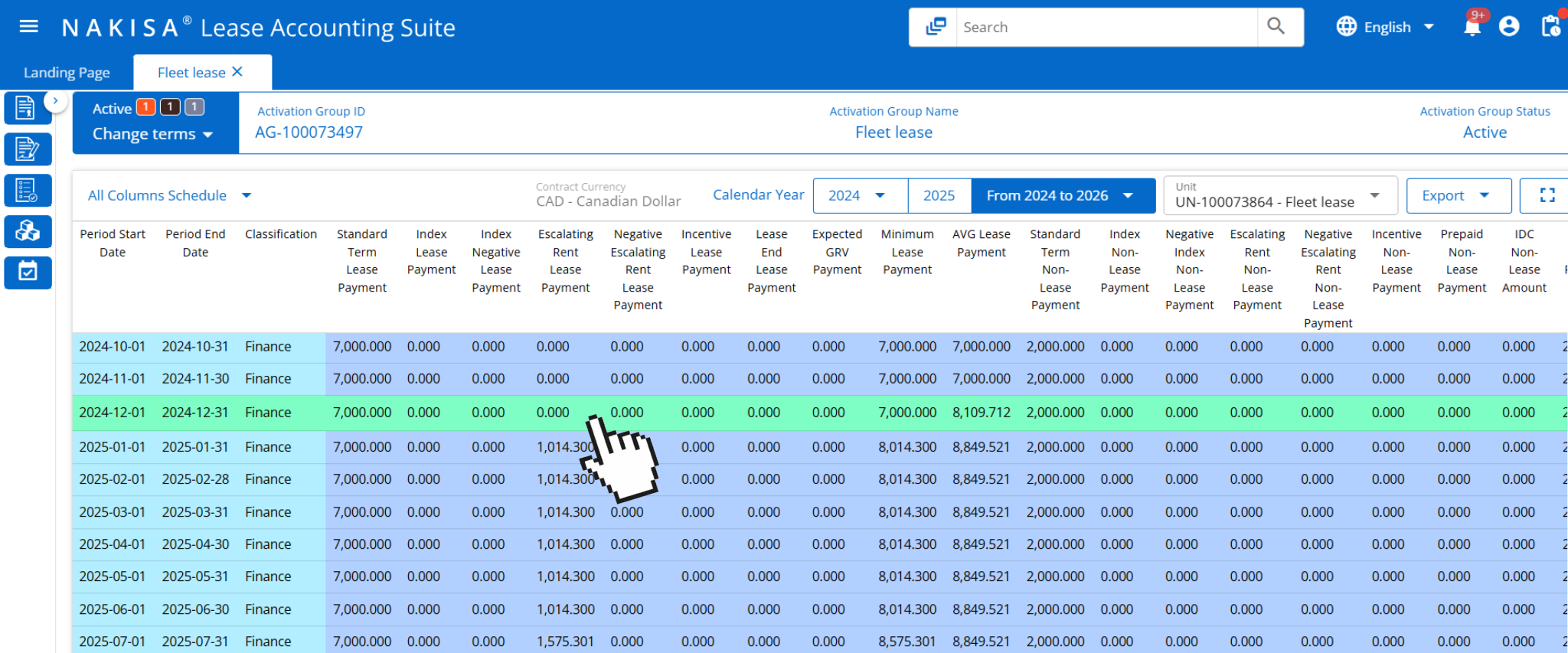
In Nakisa’s all-column schedule, users can track and view details of the exercised event highlighted in the green row.
- Advanced CPI and commodity index management: Nakisa Lease Management (NLM) and Nakisa Lease Accounting (NLA) together provide manufacturers with powerful tools to manage indexation at scale. NLM enables the creation of custom CPI and commodity-based indices, such as energy or steel prices, using formula-driven logic that blends multiple variables. This is particularly useful for facilities or equipment leases where rent escalates based on raw material market trends. NLA complements this with Conditional Indexation, allowing users to define floor and ceiling limits within lease agreements, ensuring that index-based adjustments align with internal financial policies and regional compliance needs.
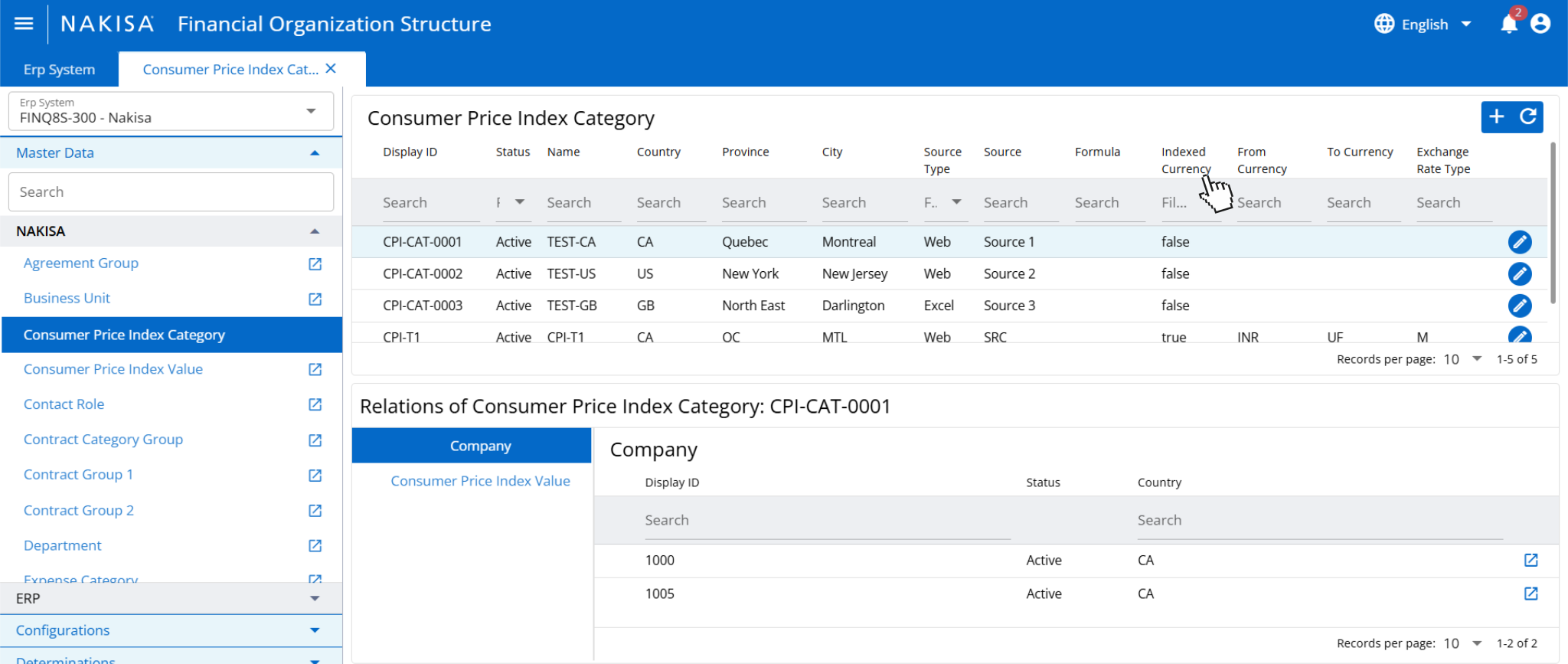
In Nakisa’s Financial Organization Structure, users can define information related to the consumer price index category.
- Seamless handling of renewals and event-based escalations: Manufacturing leases often involve multi-year commitments that may be renewed or renegotiated based on production demand or equipment upgrades. Nakisa Lease Accounting automatically recalculates lease terms during renewals, modifications, or early terminations, incorporating revised escalation clauses such as updated index-based rates or redefined fixed payment schedules. This ensures accurate remeasurement of lease liabilities and ROU assets, minimizing errors and ensuring compliance during transition periods.
Case study: Sanimax achieves 80+ hours/month in time savings with Nakisa Lease Accounting
Before adopting Nakisa Lease Accounting (NLA), Sanimax faced increasing complexity in managing its lease portfolio across North and South America. Compliance with ASC 842, manual lease administration, and a high volume of transportation and equipment leases required a more robust and automated solution. The company needed a system that ensured compliance, simplified financial reporting, and reduced manual effort. Here are some key details that illustrate the scope of their lease management needs:
- Company operations: Over 20 locations across Canada, the U.S., Brazil, and Colombia
- Types of assets: Primarily fleet, with some equipment and real estate
- ERP system: M3
- Previous lease accounting solution: Excel tools
After implementing Nakisa Lease Accounting, Sanimax automated monthly lease entries, year-end reporting, and compliance processes across all its entities. The solution significantly reduced manual work, saving up to 80 hours per month per user while improving accuracy and audit readiness. Nakisa’s user-friendly interface and robust reporting capabilities gave Sanimax complete confidence in its lease data.
The cloud-based software streamlined key workflows, including contract creation and financial statement generation, and improved responsiveness during financial close periods. Ongoing upgrades and dedicated support from Nakisa’s team further enhanced the user experience and deepened the partnership between the two Montreal-based companies.
Challenge 3: Complex manufacturing lease structures
Lease arrangements in manufacturing often go beyond straightforward rentals. As manufacturers grow across borders and expand their operational models, they routinely engage in lease scenarios that are anything but conventional. These complexities stem from embedded lease elements in service agreements, situations where the organization is both a lessee and lessor, or contracts with atypical payment structures such as prepayments. These structures present serious challenges in terms of lease identification, classification, and ongoing compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
Embedded leases
In the manufacturing industry, lease obligations are not always obvious. Many long-term operational agreements such as contract manufacturing, dedicated warehousing, or outsourced logistics, can include the use of specific assets that qualify as leases under IFRS 16 and ASC 842. These embedded leases are often hidden within broader service or supply contracts, making them difficult to identify and account for correctly. According to a KPMG survey of mostly Fortune 1000 companies, identifying embedded leases is the biggest challenge under the new accounting standards. The process of identifying all leases, especially those embedded within service or supply contracts, was described as a significant undertaking. Failure to recognize and separate these components can result in misstatements and non-compliance with accounting standards. Below are some of the key challenges manufacturers face when managing embedded leases.
- Identification of embedded lease components in operational contracts: Manufacturers frequently engage in long-term outsourcing or service agreements such as contract manufacturing or dedicated logistics operations, that may involve the exclusive use of equipment, warehouses, or production lines. Identifying whether these agreements convey control over specific assets is critical for determining if an embedded lease exists under IFRS 16 or ASC 842.
- Separation of lease and non-lease components: Once an embedded lease is identified, accountants must unbundle lease payments from the broader service agreement. Allocating contract payments accurately between lease and non-lease components is a complex task, particularly when these agreements include bundled services like staffing, maintenance, or utilities.
- Ongoing monitoring and reassessment: Manufacturing contracts can span multiple years and may be amended over time to reflect changes in output levels, asset usage, or pricing terms. Each modification requires a reassessment of the lease component and potential remeasurement of lease liabilities and the associated ROU asset, demanding continuous contract oversight to maintain compliance.
- Jurisdictional and operational complexity: Global manufacturers often negotiate these agreements across multiple legal jurisdictions, where contract terms, interpretation of control, and regulatory nuances differ. This amplifies the difficulty of consistent lease identification and accounting treatment across the portfolio.
How Nakisa solves embedded lease challenges for global manufacturers
Nakisa Lease Accounting helps manufacturing organizations manage the complexities of embedded leases often found in operational and supply agreements by offering a suite of intelligent tools and automation:
- AI-powered lease abstraction: The Nakisa AI Agent for document abstraction streamlines the identification of embedded leases in complex manufacturing contracts, such as long-term outsourcing or contract manufacturing agreements. It automatically extracts key lease terms like exclusive equipment use, duration, and conditions from agreements, consolidating this information into a centralized platform. This reduces manual effort, mitigates the risk of missed obligations, and ensures compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
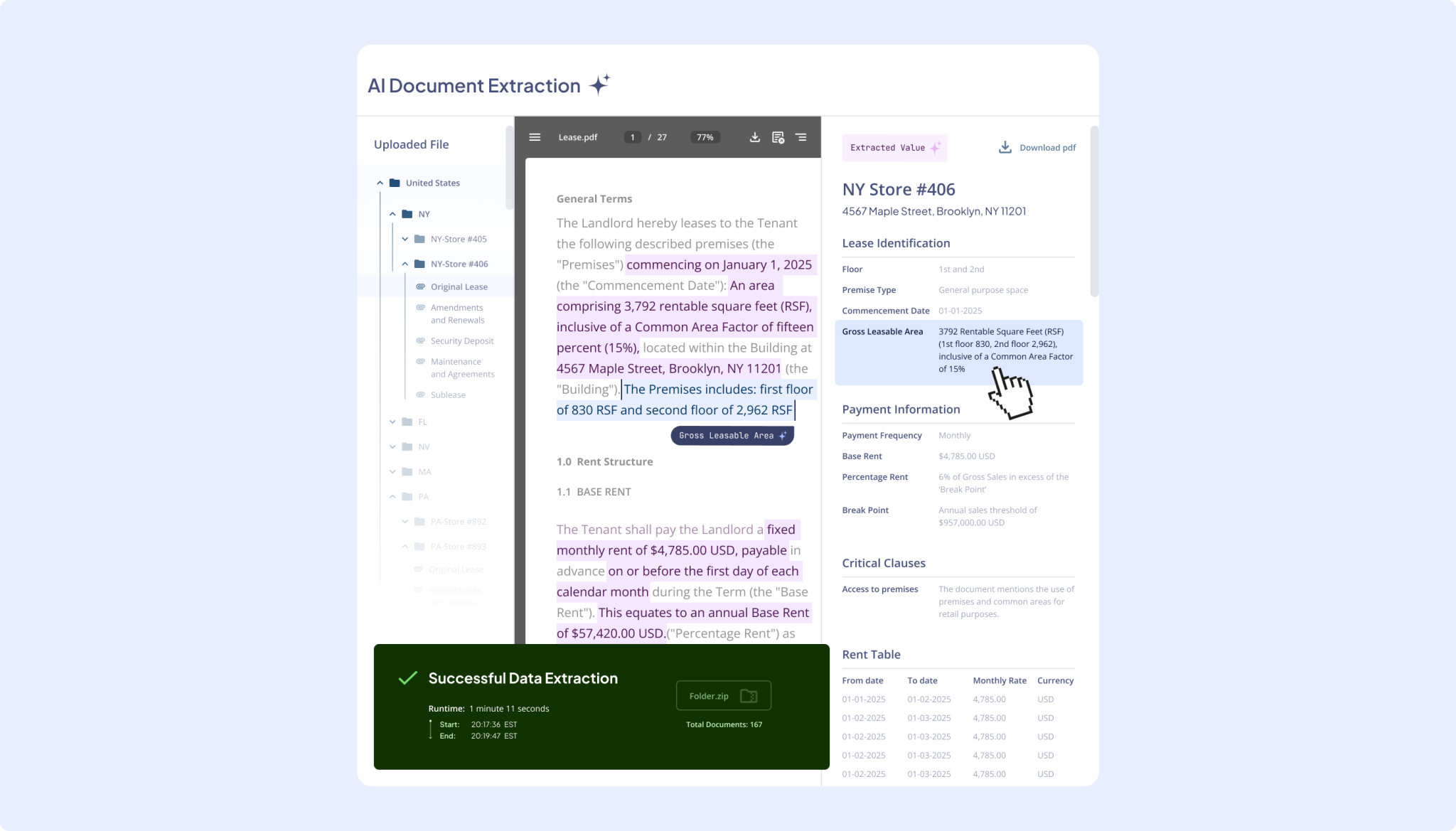
In Nakisa Lease Accounting, users can interact with an AI Agent for document abstraction to extract key lease terms.
- Separation of lease and non-lease components: Once embedded lease components are identified within broader manufacturing contracts, Nakisa automates the separation process. It allocates payments between lease and service components accurately, supporting proper capitalization and ensuring the correct application of lease accounting standards. This functionality is particularly useful in multi-element arrangements, where equipment use is bundled with services such as maintenance or operational staffing.
Nakisa Lease Accounting software supports non-lease components with dedicated fields and tailored calculations that adapt to the user's specific needs.
- Ongoing monitoring and adjustment: Manufacturing contracts often evolve with new terms, changes in asset control, or contract modifications. Nakisa enables continuous monitoring of these agreements, automatically flagging changes that could affect lease classification or require remeasurement. This proactive tracking helps finance teams maintain accuracy and compliance over time, even as operations scale across multiple plants, jurisdictions, or production lines.
From embedded leases in equipment-sharing contracts to dedicated facilities embedded in supply agreements, Nakisa helps manufacturers maintain visibility, automate compliance, and reduce manual complexity across their lease portfolio.
Alanna Bilben
Business Transformation IT RTR Lead at 3M
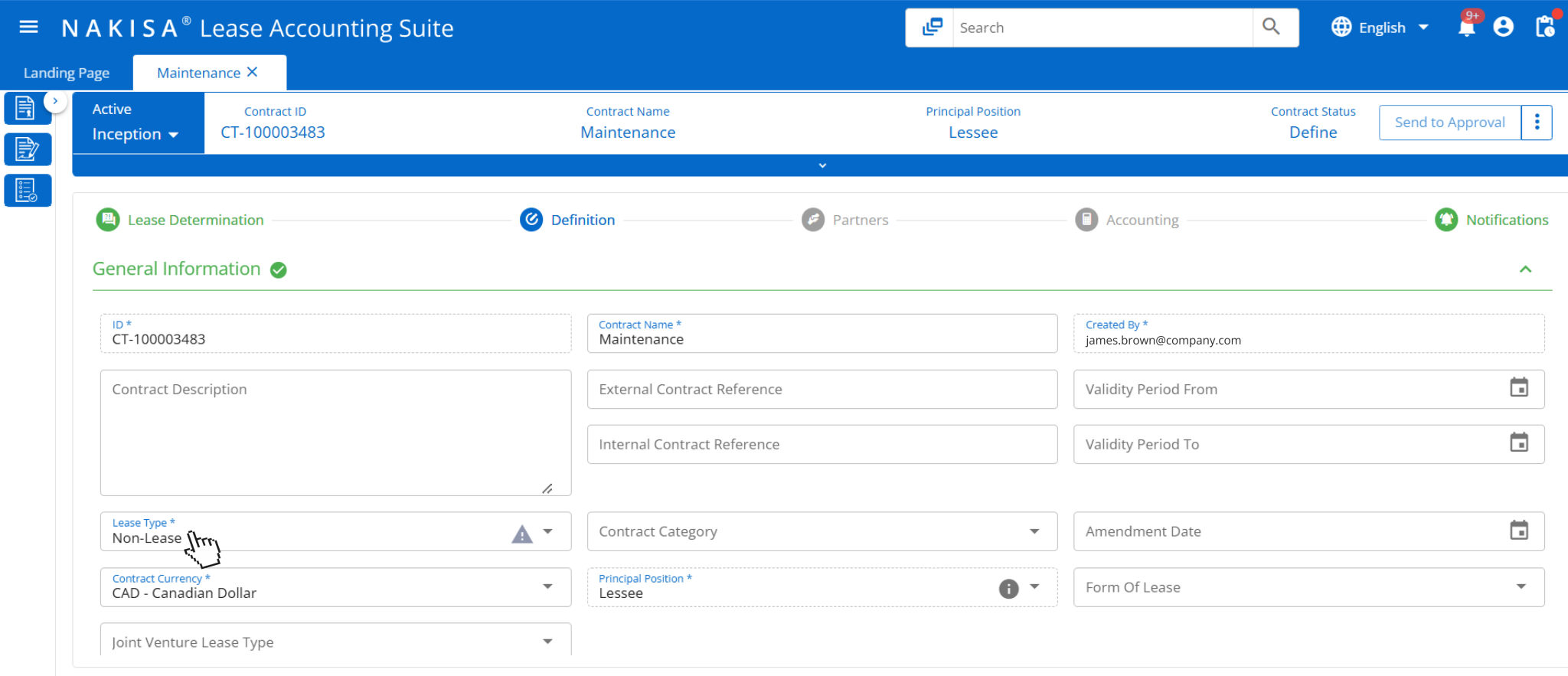
Subleasing arrangements
Subleasing is another area that complicates lease management in manufacturing. Manufacturers may sublease unused space or idle machinery to vendors, logistics partners, or third parties to recover costs. This puts the company in the dual position of being both lessee and lessor. These sublease arrangements introduce layers of complexity: separate income recognition, new lease classification assessments, and the need to remeasure lease terms if the sublease changes expectations for the original lease. Here are the key challenges manufacturers face in such arrangements:
- Dual roles as lessee and lessor: Subleasing arrangements place the manufacturer in a dual role: leasing from a property owner or equipment provider while subleasing to another party. These roles require separate accounting treatments for lease liabilities (as a lessee) and lease receivables or income (as a lessor), significantly increasing the complexity of financial reporting.
- Head lease and sublease accounting considerations: When a manufacturer subleases a portion of a facility or piece of equipment, it must assess the impact on the original (head) lease. If the sublease results in a reduction in the scope of the head lease, this may trigger a lease modification requiring remeasurement of the ROU asset and lease liability. At the same time, the sublease must be accounted for as a separate lease arrangement. Proper assessment and treatment are critical to ensure compliance and avoid misstatements in financial reporting.
- Compliance with lease modifications: If subleasing triggers amendments to the original lease such as changes in term length or payment structure, manufacturers must perform additional calculations to maintain compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842. This adds to administrative workload and raises the risk of accounting errors, especially in multi-asset or multi-jurisdiction contracts.
How Nakisa solves subleasing arrangements challenges for global manufacturers
Manufacturers navigating subleasing arrangements, whether for excess warehouse space, specialized equipment, or production areas, can rely on Nakisa Lease Accounting to streamline dual-role lease management and ensure compliance with evolving standards. Here's how:
- Head lease and sublease visibility for industrial operations: Nakisa enables manufacturers to effectively manage complex lease structures when acting as both lessee and lessor. In scenarios where a portion of a facility or equipment is subleased, Nakisa separates the head lease and sublease into distinct contracts, providing clear visibility and control over each arrangement. The solution ensures compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 by supporting appropriate accounting treatment and reporting from both the lessee and lessor perspectives. Automated schedules, event-driven accounting, and comprehensive reporting features help manufacturers maintain compliance while simplifying ongoing lease management.
Nakisa’s lessor accounting module supports operating leases and handles calculations efficiently.
- Automatic head lease reassessment and sublease handling: When a manufacturer subleases a portion of a leased asset, Nakisa Lease Accounting automatically recalculates the right-of-use (ROU) asset and lease liability to reflect any reduction in scope of the head lease. Simultaneously, a separate sublease contract is created, providing visibility and control from both the lessee and lessor perspectives. This integrated approach minimizes the risk of misstatements and ensures accurate financial reporting in compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
- Seamless visibility across head lease and sublease: Nakisa simplifies sublease management by allowing users to link subleases directly to the corresponding head lease within the system. This connection ensures consistency in asset classification and provides a clear audit trail between lessee and lessor positions. By centralizing visibility, manufacturers can reduce manual tracking efforts and improve control across their lease portfolio.
Prepaid leases
Prepaid leases in manufacturing present unique challenges, especially when substantial upfront payments are made for long-term access to strategic facilities. These arrangements require careful handling to ensure compliance with accounting standards and accurate financial reporting, particularly regarding timing mismatches, amortization of assets, and future escalations. Let’s explore how these challenges impact lease accounting and how they can be managed effectively.
- Timing mismatches in payments and lease terms: Prepaid leases often involve significant upfront payments, but the lease term may not begin immediately. This can create timing mismatches in financial reporting when payments are made in one fiscal year, but the lease term starts in another, complicating expense recognition and financial statements.
- Amortization of the right-of-use (ROU) asset: Regardless of the upfront payment, manufacturers must amortize the right-of-use (ROU) asset over the full lease term. Ensuring that this amortization aligns with the actual lease term, even when the payment is made early, adds complexity to the accounting process.
- Escalations and future adjustments: Prepaid leases may include provisions for future escalations or rent increases. These need to be reflected accurately in the valuation of the asset, creating additional challenges in lease liability calculations and ongoing financial reporting.
- Compliance with accounting standards: Under IFRS 16 and ASC 842, the upfront payment for a prepaid lease is recognized as part of the right-of-use (ROU) asset, not the lease liability. The full lease obligation must still be recognized based on the present value of future lease payments. Improper handling of prepaid leases, such as misclassifying the upfront payment, can lead to misstatements on the balance sheet and incorrect expense recognition, potentially causing non-compliance with accounting standards.
How Nakisa solves prepaid leases challenges for global manufacturers
Prepaid leases in manufacturing can introduce complexities, particularly when substantial upfront payments are made for strategic locations or specialized facilities. These leases require careful management to ensure compliance with accounting standards. Under IFRS 16, while the full lease obligation must be recognized, the upfront payment is treated as an addition to the right-of-use (ROU) asset. The ROU asset is then amortized over the lease term. Challenges arise from timing mismatches between payments and lease terms, as well as adjustments due to escalation clauses. Let’s explore how Nakisa Lease Accounting helps manufacturers navigate these complexities with efficient, compliant solutions.
- Accurate lease liability and ROU asset management: Nakisa ensures that the full lease liability is recognized based on the present value of future lease payments, while the right-of-use (ROU) asset is correctly adjusted to include any prepaid amounts. The software automatically tracks and amortizes the ROU asset over the lease term, regardless of the timing of upfront payments, ensuring full compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
- Timing adjustments and financial reporting: Nakisa Lease Accounting allows manufacturers to manage the timing mismatches that can occur when lease payments are made in one fiscal year, but the lease term begins in another. The system ensures that these payments are appropriately reflected in financial statements, preventing misstatements in expense recognition and balance sheet representation.
- Escalation handling: When prepaid leases include fixed or index-based rent escalations, Nakisa ensures these are incorporated into the initial or subsequent measurement of the lease liability and right-of-use (ROU) asset, as applicable. The system tracks escalation clauses, whether contractual or tied to indices like CPI, and automatically updates calculations to reflect changes in future lease payments. This ensures accurate financial reporting and alignment with contract terms, even in prepaid lease scenarios.
Irene Garcia
Assistant Corporate Controller at Sanimax
Challenge 4: Lease reassessment for global manufacturers
For global manufacturers, managing lease reassessment during key events such as lease termination, extensions, rent adjustments, buy-out options, impairments, and retirements presents significant challenges. These events necessitate a careful evaluation of lease terms, financial obligations, and the need for adjustments to lease accounting. Manufacturers must ensure these adjustments comply with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 accounting standards. Here's how key reassessment events impact lease management:
- Lease termination: When a lease is terminated, manufacturers must reassess the remaining lease term and adjust associated liabilities accordingly. Terminations often involve early exit fees, penalties, or adjustments based on lease agreement terms. Accurately reflecting these changes in financial statements is essential to maintain compliance with accounting standards.
- Lease extensions: Lease extensions require recalculating the lease term to determine whether the extension is enforceable under the lease agreement. Manufacturers must adjust the right-of-use (ROU) asset and lease liability to reflect the extended term. This often involves recalculating future payments, including rent escalations, variable payments, and other costs related to the lease. Understanding the practical enforceability of the extension is key to accurate accounting.
- Lease indexation: Lease indexation, where rental payments are adjusted based on external indices (e.g., the Consumer Price Index), can be complex for manufacturers to manage. Under IFRS 16 and ASC 842, manufacturers must reassess lease liabilities and ROU assets whenever index-linked rent changes occur. This requires tracking changes in index rates and adjusting financial obligations accordingly.
- Buy-out option: If a lease includes a buy-out option, manufacturers must evaluate whether exercising this option is "reasonably certain" to occur. Once exercised, the lease is reclassified as a finance lease, and the leased asset is transferred to an owned asset. This requires forecasting future cash flows, assessing the likelihood of buy-out, and recalculating the lease liability and ROU asset accordingly.
- Rent reduction: Rent reductions often lead to lease modifications that require careful evaluation. If rent is reduced, manufacturers must determine whether the change constitutes a lease modification, which could affect the lease liability and ROU asset. Adjustments must account for revised payment schedules, discount rates, and any other material changes to the lease agreement. Accurate reporting of modified terms ensures compliance with accounting standards.
- Impairment: Lease impairment occurs when the recoverable amount falls below the carrying value of the ROU asset, such as when a leased asset no longer provides anticipated economic benefits. Manufacturers must assess and measure impairment based on current market conditions, making the necessary adjustments to reflect this impairment in their financial statements.
- Retirement: A retirement is an event in accounting where an asset, including a leased asset, is removed from service, often due to it being sold, scrapped, or fully depreciated. Retirements affect the lease accounting process, as manufacturers need to adjust for the asset’s removal and ensure proper derecognition of any remaining value in their financial statements. This event can impact both lease liabilities and ROU asset balances and may result in the recognition of gains or losses.
Managing these reassessment events requires manufacturers to have robust systems in place to evaluate lease modifications, ensure accurate accounting, and maintain compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842. Effective lease management systems can help navigate these challenges efficiently, ensuring that all lease changes are captured accurately and in a timely manner.
How Nakisa solves lease reassessment challenges for global manufacturers
Managing lease reassessments is a significant challenge for global manufacturers, especially when navigating complex lease events like terminations, extensions, rent reductions, impairments, and retirements. These events require careful evaluation and recalibration of financial obligations, often across a large portfolio of leases. Nakisa Lease Accounting simplifies these complexities, ensuring compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 while streamlining the management of critical lease events. Here's how Nakisa addresses these challenges.
- AI-powered lease abstraction: Nakisa’s AI-driven lease abstraction tool plays a crucial role in simplifying complex lease agreements for manufacturers. The tool automatically extracts and organizes key lease data, making it easier to track various lease terms, renewal options, and clauses, especially for manufacturers dealing with multi-layered or non-standard lease structures. By centralizing all relevant lease information in one database, manufacturers can quickly access critical details, reducing the need for manual data entry. This minimizes the risk of errors and ensures that important lease obligations, such as early termination penalties or extensions, are never overlooked, promoting both efficiency and compliance.
- Event management: Nakisa Lease Accounting supports the creation and management of events like impairment, terminations, and modifications. The platform provides fields to input key event details, such as modification reasons, dates, and asset impairment losses, ensuring that manufacturers can easily track and manage significant lease events.
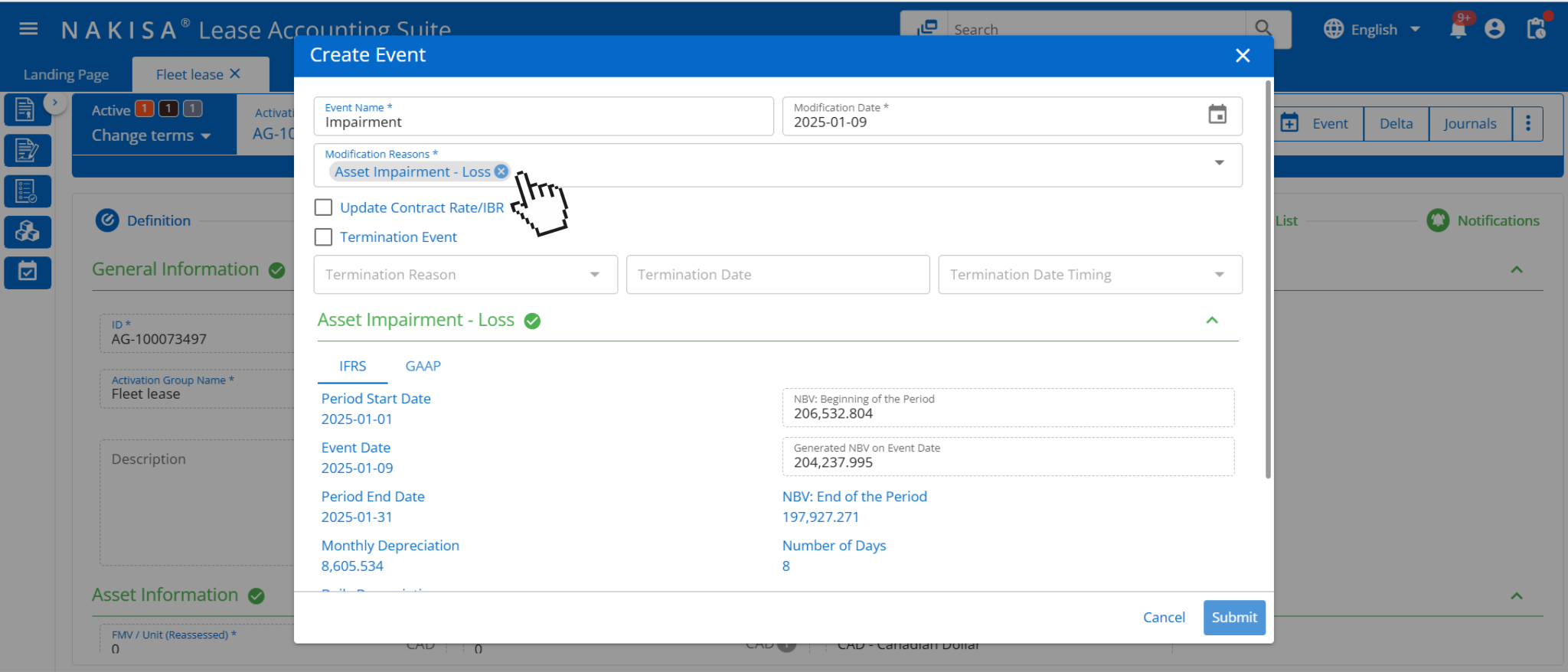
Nakisa Lease Accounting supports event creation and management such as impairment. The interface displays fields such as modification reasons, modification date, and asset impairment loss.
- Critical date and event tracking: Nakisa Lease Accounting offers robust tracking capabilities that help manufacturers stay on top of important milestones throughout the lease lifecycle. The software enables businesses to monitor key events such as lease termination, extension, indexation, buy-out options, rent reductions, and impairments in real-time. It also provides a comprehensive portfolio summary of due lease and non-lease payments for the current, next, and upcoming months, enhancing accuracy in forecasting and budgeting. This proactive approach helps manufacturers avoid missing any critical events and ensures compliance with accounting standards.
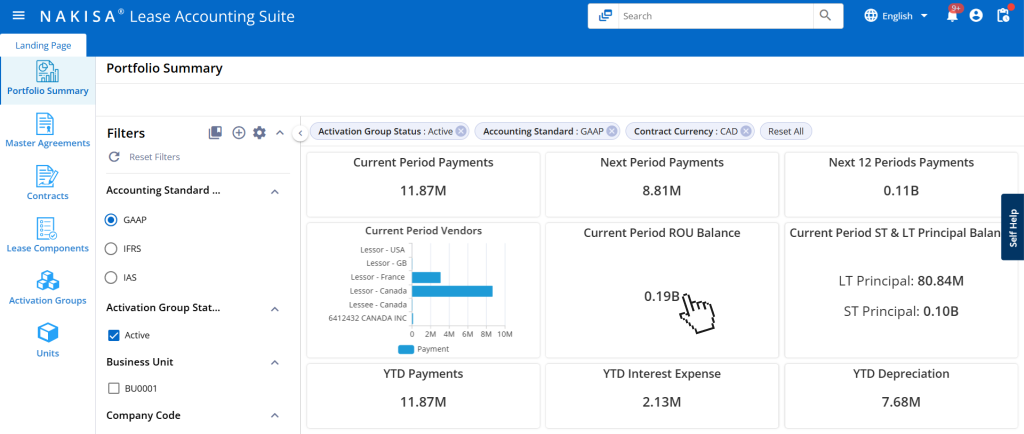
Nakisa Lease Accounting provides a portfolio summary of due lease and non-lease payments for the current month, next month, and the next 12 months.
- Mass event management tool: Nakisa’s mass event management feature allows manufacturers to efficiently manage simultaneous adjustments to multiple lease components. Whether updating terms or applying changes affecting right-of-use (ROU) assets and liabilities, this tool streamlines the process, saving time and ensuring that the updates are applied consistently and accurately across the portfolio.
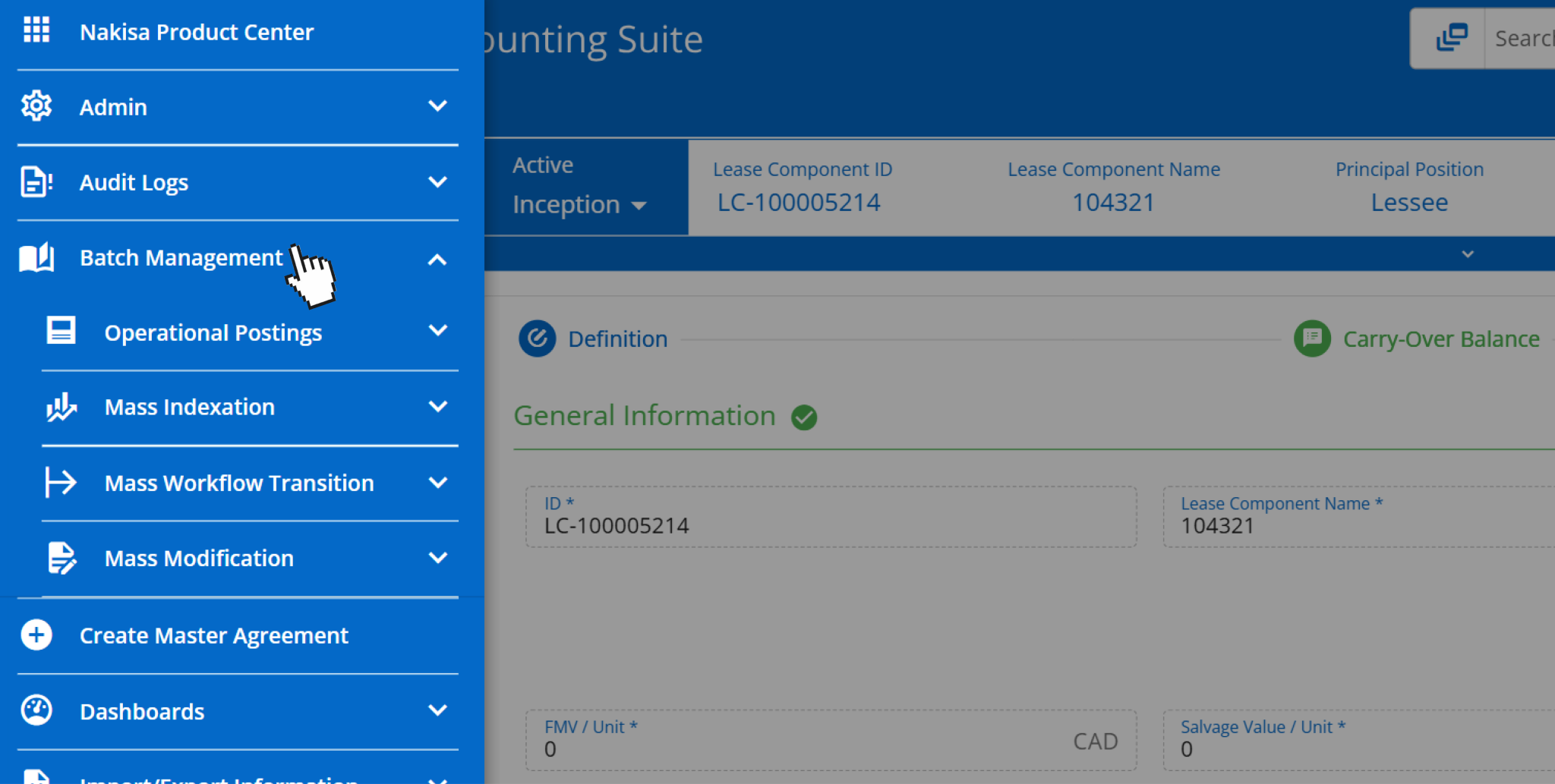
In Nakisa Lease Accounting software, users can perform batch management operations such as mass indexations, mass workflow transitions, and mass modifications.
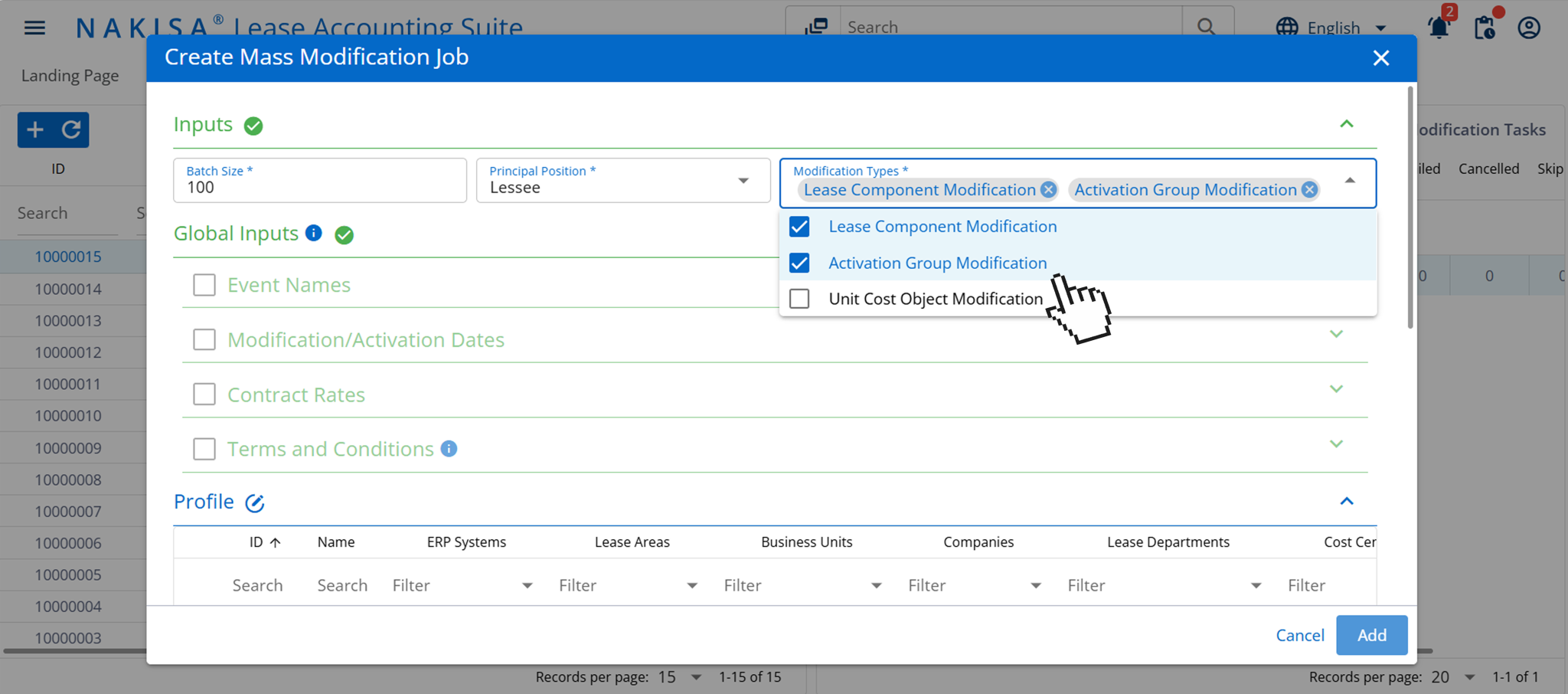
In Nakisa Lease Accounting software, users can perform mass modification jobs.
- Recalculation and adjustment tools: Nakisa’s automated recalculation and adjustment tools ensure that lease liabilities and ROU assets are updated in response to critical lease events, such as modifications or terminations. These tools streamline workflows, eliminating manual interventions, and keeping lease data accurate and compliant with accounting standards. Manufacturers can efficiently manage lease data recalculations, ensuring that their accounting remains precise and up to date, even as lease terms change.

By leveraging Nakisa's advanced lease accounting capabilities, manufacturers can effectively manage the complexities of lease reassessments, ensuring compliance with accounting standards and maintaining efficient, accurate lease portfolios.
Jane Yi
Financial Analyst at EMCO
Challenge 5: CAM, insurance, and tax reconciliation for global manufacturers
For global manufacturers, effective management of non-lease components such as Common Area Maintenance (CAM) costs, insurance premiums, and property taxes is essential for maintaining accurate financial records. CAM expenses, often shared between landlords and tenants, are a key aspect of multi-tenant properties and include costs for shared spaces like parking lots or hallways. In addition to CAM costs, manufacturers must ensure that insurance premiums and property taxes related to the leased property are properly allocated between the landlord and tenants. Proper tracking and allocation of these non-lease components are crucial for accurate financial reporting and reducing the risk of errors, particularly in complex lease structures. Key challenges in managing non-lease components include:
- Distinguishing lease vs. non-lease components: Correctly classifying CAM, insurance, and tax expenses as lease or non-lease components is crucial for accurate financial reporting and managing lease liabilities and ROU assets under IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
- Variable CAM expenses and lease reassessments: CAM costs can fluctuate annually based on property operating expenses, and while these are generally treated as non-lease components, manufacturers must regularly reassess lease liabilities and the associated ROU asset if the lease includes variable lease payments tied to CAM or similar expenses. This ensures that any changes in these variable payments are accurately reflected in the financial records, supporting compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842.
- Reconciliation with non-standard accounting calendars: Global manufacturers often use customized accounting calendars, such as the 4-4-5 or 13-period calendar, to align with their operational cycles. This requires tailored reconciliation processes for CAM, insurance, and tax costs, as well as rent payments and other variable costs.
How Nakisa solves CAM, insurance, and tax reconciliation challenges for global manufacturers
Nakisa Lease Accounting and Nakisa Lease Management offer powerful solutions for global manufacturers to manage the complexities of lease reconciliation, particularly for Common Area Maintenance (CAM), insurance, and tax costs. Here's how Nakisa helps:
- Lease reconciliation management: Nakisa Lease Management simplifies managing shared expenses, such as CAM, tax, and insurance charges. Manufacturers can upload charges in bulk using the mass import tool, enabling quick and accurate reconciliation. The software supports uploading invoices from landlords, which automatically populate CAM, tax, and insurance charges for the year. This process helps track accrued expenses against total costs, taking lease conditions (like pro-rata shares, expense caps, and limits) into account. Nakisa also helps resolve vendor invoice discrepancies and disputes across multiple leases, enhancing efficiency and ensuring accurate billing.
- Lease and non-lease components classification: Nakisa Lease Accounting allows users to easily classify CAM, insurance, and tax costs as lease or non-lease components, ensuring compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842. It offers flexibility in categorizing CAM expenses, treating them as part of the lease or separate non-lease items. Maintenance costs, for example, can be included in the base rent, while other services like marketing are classified as non-lease expenses. This functionality helps reduce the risk of misclassification and ensures accurate expense allocation.
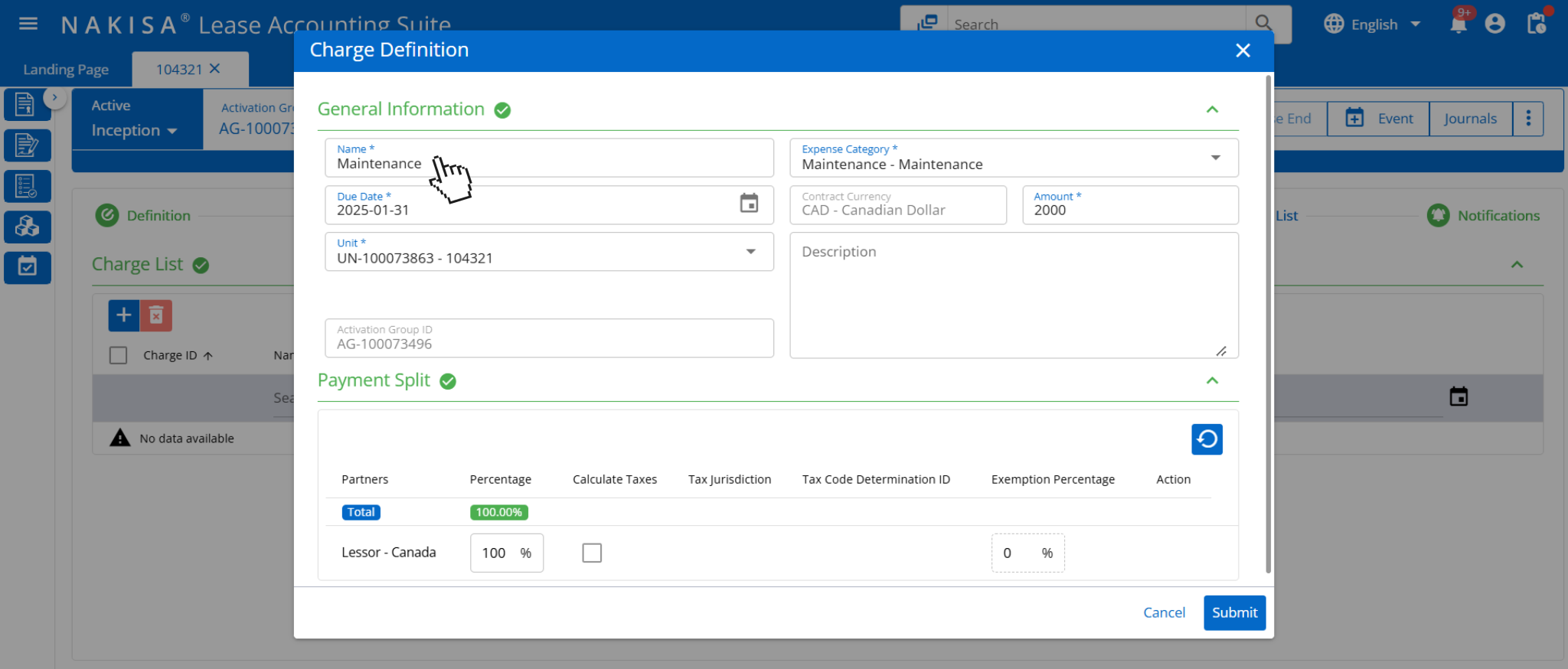
In Nakisa’s software, additional expenses such as maintenance can be defined within the Charge Definition functionality.
- Audit trails and visibility for CAM, insurance, and tax costs: Nakisa Lease Accounting ensures transparency by providing detailed audit trails for non-lease components such as CAM, insurance, and property taxes. This enhances visibility into the allocation and tracking of these costs, helping manufacturers maintain accurate records and ensuring compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842. With Nakisa, manufacturers can easily access historical data and support documentation for these costs, simplifying audits and reducing the risk of errors in financial reporting.
- Efficient management of variable CAM expenses: With Nakisa Lease Accounting, manufacturers can track and update variable CAM expenses over time. Automated lease reassessments and proactive notifications keep users on top of any fluctuations, ensuring that lease liabilities and operating expenses remain accurate, even as costs change.
By offering these features, Nakisa Lease Accounting helps global manufacturers streamline their processes, enhance accuracy, and maintain compliance while managing the complexities of CAM, insurance, and tax costs, ensuring efficient lease reconciliation.
Challenge 6: Taxation in the manufacturing industry
Manufacturers, particularly those operating on a global scale, face considerable challenges in managing tax obligations across their lease portfolios. With complex, region-specific tax regulations and varying lease types, ensuring compliance and accuracy can be an overwhelming task. The dynamic nature of lease agreements, including modifications and updates, adds another layer of complexity to tax management.
- Multi-jurisdictional compliance: Manufacturers must navigate the complexities of different tax regulations across regions. With operations spanning multiple countries, maintaining compliance in each jurisdiction requires constant monitoring and adjustment of tax obligations.
- Complex tax laws: Manufacturers must adhere to intricate tax laws, such as VAT and sales tax, which may vary in terms of treatment depending on location. These regulations are subject to frequent changes, adding complexity to tax calculations for each lease.
- Tax calculation accuracy: Given the complexity of managing tax obligations for large portfolios with diverse lease structures, manual tax calculations can lead to errors, inefficiencies, and increased risk of penalties or audits. Automated, accurate tax reporting is crucial for staying compliant and avoiding costly mistakes.
- Recalculation due to lease modifications: Any changes in lease terms, such as renewals, terminations, or alterations, can affect the tax treatment of leases. Manufacturers need to ensure timely recalculations of tax obligations to maintain accuracy and avoid discrepancies in their tax filings.
Taxation is a critical challenge in managing leases for global manufacturers, and keeping track of these complexities is essential for ensuring accurate and compliant financial reporting.
How Nakisa solves taxation challenges for global manufacturers
Nakisa Lease Accounting provides a comprehensive solution to the taxation challenges global manufacturers face, offering automation, real-time updates, and seamless integration to ensure compliance with complex tax laws across various jurisdictions. Here's how Nakisa addresses these challenges:
- Multi-jurisdictional tax management: Nakisa’s software enables manufacturers to manage tax obligations, including VAT and sales tax, across different jurisdictions. The system allows for flexible tax settings, such as configuring tax and no-tax jurisdictions for each country and linking the correct company codes to their respective countries. This ensures tax treatments are customized to regional requirements, providing an accurate and compliant tax solution. Additionally, tax amounts are incorporated into journal entries and displayed alongside vendor payments, giving a comprehensive view of all tax-related transactions.
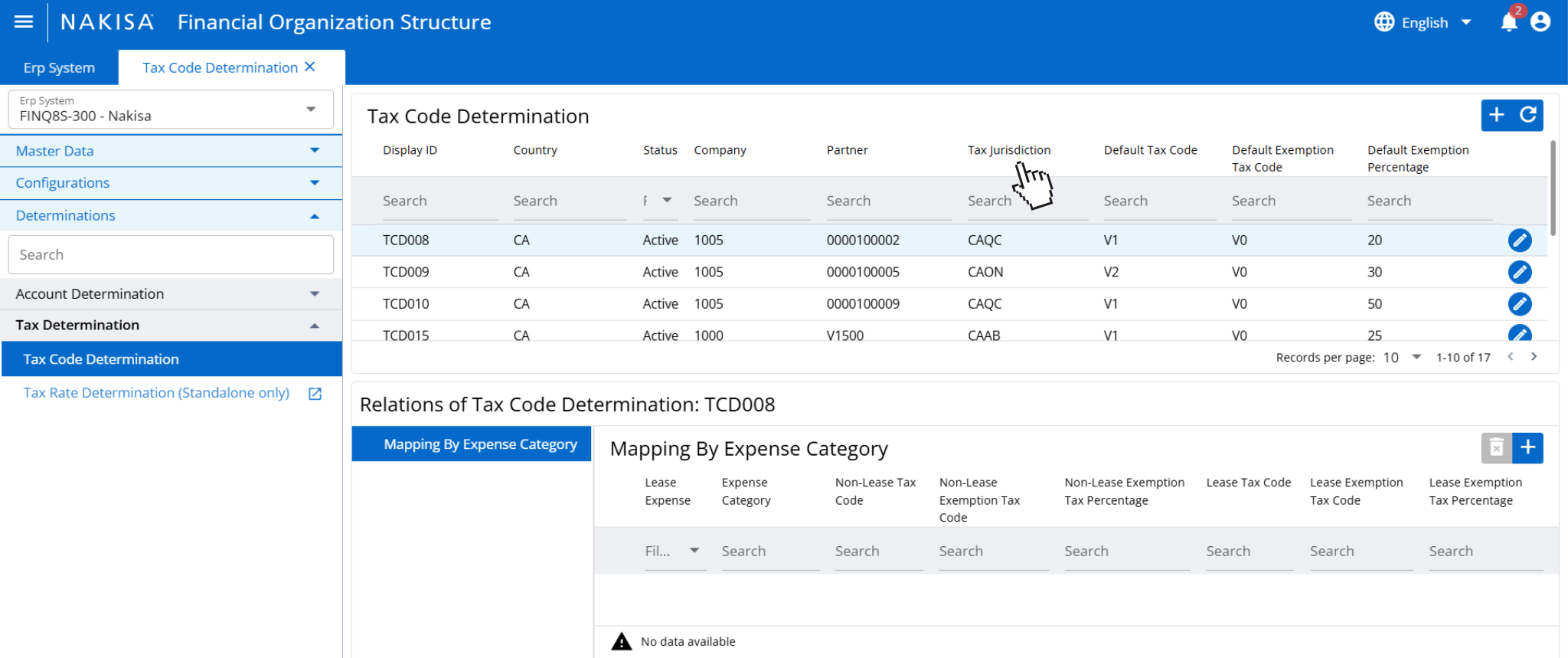
In Nakisa’s Financial Organization Structure, users can configure information related to the tax code determination.
- Flexible tax treatment configuration: Nakisa’s software allows manufacturers to configure tax treatments based on various factors like jurisdictions, tax codes, tax rates, countries, company codes, and exemption rates. This flexibility ensures that tax calculations align with local tax regulations, optimizing tax strategies and minimizing the need for manual adjustments.
- Automated tax calculations and adjustments: Nakisa automates tax calculations based on jurisdiction, reducing the manual effort required. The system automatically adjusts tax obligations as lease terms change whether due to renewals, modifications, or terminations, while ensuring accurate tax reporting and reducing the risk of underreporting or overreporting.
- Real-time tax updates: Nakisa provides real-time updates to lease data, ensuring tax obligations are always based on the most current lease terms. Any lease modifications or renewals trigger automatic recalculations of taxes, keeping tax records accurate and up to date without requiring manual intervention.
Taxation can be a complex and burdensome challenge for global manufacturers, with varied tax laws and a need for consistent updates. Nakisa Lease Accounting simplifies these complexities by automating tax calculations, ensuring compliance with evolving regulations, and offering flexible tax treatment. This unified approach helps manufacturers reduce errors, improve efficiency, and stay compliant with minimal effort.
Valerie Leffray
Global Business and Functions Director at Grupo Gondi
Challenge 7: Compliance with accounting standards for global manufacturers
For global manufacturers, adhering to accounting standards like IFRS 16, ASC 842, and local GAAP is crucial but challenging. These standards require strict rules for lease classification, recognition, and reporting, especially for manufacturers managing complex and diverse lease portfolios. The key challenges include:
- Accurate lease classification: Leases must be properly classified as either finance or operating leases. Misclassifications can lead to incorrect financial reporting, potential penalties, and reputational damage. Manufacturers often struggle to interpret lease terms, particularly with embedded leases or complex payment structures.
- Non-lease components identification: Identifying and separating non-lease components, such as maintenance or services, from the lease itself can be tricky. Including these components incorrectly as part of the lease can result in inaccurate asset and liability calculations, which may lead to non-compliance with accounting standards.
- Lease data centralization and accuracy: Manufacturers often manage leases across multiple locations and jurisdictions, and consolidating lease data for compliance is both time-consuming and error-prone. Incomplete or missing data can lead to non-compliance during audits, creating risks for the organization.
- Financial reporting and disclosure requirements: Under IFRS 16 and ASC 842, nearly all leases must be recognized on the balance sheet, with the right-of-use (ROU) asset and corresponding lease liability recorded at commencement. This eliminates the historical off-balance-sheet treatment for most operating leases. In addition to recognition, both standards require extensive qualitative and quantitative disclosures, including maturity analyses of lease liabilities, breakdowns of lease expenses, discount rates used, and narrative explanations of significant leasing arrangements.
- Handling lease modifications, renewals, and terminations: Any changes to lease terms, including modifications, renewals, or terminations, have a significant impact on compliance. Manufacturers must reassess and adjust ROU assets and liabilities to reflect these changes, ensuring accurate financial reporting. Failure to capture and update these changes in accordance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 could result in material misstatements or audit findings.
How Nakisa ensures compliance with accounting standards for global manufacturers
Nakisa Lease Accounting empowers global manufacturers to ensure compliance with IFRS 16, ASC 842, and local GAAP. Here’s how Nakisa simplifies the process of meeting these complex standards:
- Parallel compliance with ASC 842, IFRS 16, and Local GAAP: Nakisa’s software allows manufacturers to seamlessly comply with ASC 842, IFRS 16, and local GAAP by supporting the recognition of right-of-use (ROU) assets, lease liabilities, and the efficient management of lease classifications and modifications. It enables simultaneous management of leases across all standards on a single platform, ensuring all regulatory requirements are met without duplicating efforts. The software generates disclosure reports in line with the specific standards' requirements, making compliance streamlined.
- Flexible treatment of lease and non-lease components: Nakisa’s software provides flexibility in handling both lease and non-lease components. Manufacturers can choose whether to combine or separate these components, with dedicated fields and tailored calculations that suit their needs. This flexibility is particularly important when dealing with maintenance, services, or other non-lease charges that must be accurately categorized to meet compliance standards.
Nakisa Lease Accounting software supports non-lease components with dedicated fields and tailored calculations that adapt to the user's specific needs.
- Asset-level accounting: Nakisa’s platform tracks individual assets within a lease contract, ensuring precise asset-level accounting. Each asset, with its unique lifecycle, including amortization periods, start and end dates, and events like modifications, renewals, buyouts, or terminations, is managed separately. This granular approach ensures manufacturers maintain compliance with accounting standards, while also providing detailed, audit-ready financial reports.
- Auditable reports: Nakisa generates audit-ready reports with advanced drill-down capabilities, ensuring full compliance with IFRS 16, ASC 842, and local GAAP. The platform supports the complex financial calculations required, such as the measurement of ROU assets and lease liabilities, and provides both standard and customizable reports. These include comprehensive financial statements like the Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow, as well as detailed disclosures like Asset Roll Forward, Lease Liability, and Maturity Analysis. The software also supports financial forecasting, which helps evaluate the financial impact of different lease strategies.
Interactive demo: Reports

- Event management: Nakisa efficiently handles lease modifications, renewals, and terminations, ensuring compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842. The software automatically recalculates lease terms and adjusts ROU assets and lease liabilities based on changes to clauses, payment schedules, or lease conditions in real-time. With an audit trail, manufacturers can maintain full transparency and ensure accurate financial reporting, reducing the risk of misstatements and maintaining audit readiness. This feature ensures that any changes to lease obligations are captured accurately and aligned with accounting standards.
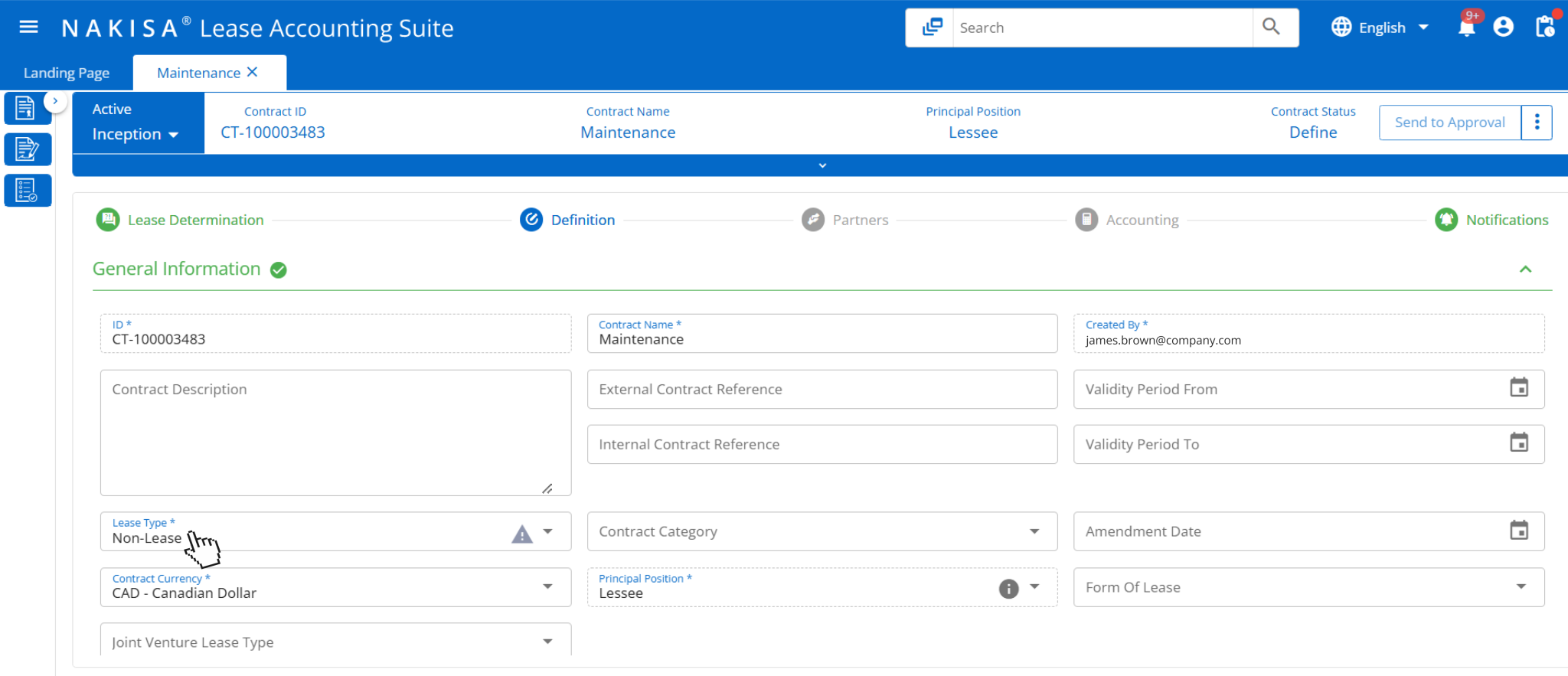
Nakisa Lease Accounting software supports event creation and management such as termination. The interface displays fields such as termination reason, termination date, and penalty amount.
By leveraging these capabilities, Nakisa Lease Accounting helps global manufacturers confidently manage their leases, ensuring they stay compliant with IFRS 16, ASC 842, and local GAAP while providing accurate and efficient financial reporting.
Case study: Grupo Gondi achieves 93% faster lease processing and IFRS 16 compliance with Nakisa Lease Accounting
Before adopting Nakisa Lease Accounting (NLA), Grupo Gondi managed thousands of lease contracts manually using Excel files. As operations expanded, managing hundreds of contracts with appendices, payments in multiple currencies, and strict compliance requirements under IFRS 16, became increasingly time-consuming and error prone. The company needed an automated, multilingual solution that could streamline workflows and integrate with SAP ERP.
- Number of contracts: 7,000+
- Types of leased assets: Real estate, warehouses, vehicles, and compressors
- ERP system: SAP ECC 6.0
After implementing Nakisa Lease Accounting, Grupo Gondi achieved 93% faster lease contract processing and ensured full compliance with IFRS 16 standards. The platform reduced contract review and journal entry generation time from 30 minutes to just 2 minutes. With support in Spanish and a user-friendly interface, adoption was smooth across teams. The solution also improved portfolio visibility, enabled accurate forecasting, and provided reliable backup and recovery capabilities, empowering the finance team to manage contracts more proactively and confidently.
Francisco Javier Chavez Espinosa
Accounting Analyst at Grupo Gondi

Challenge 8: Technology, data security, and integration limitations in the manufacturing industry
In the manufacturing industry, managing leases in compliance with IFRS 16 and ASC 842 becomes increasingly complex due to technology and integration limitations. Manufacturers often operate with multiple ERP systems, legacy solutions, and fragmented software that create barriers to seamless data flow. These integration gaps result in inefficiencies, data discrepancies, and increased manual intervention, complicating lease accounting processes. Additionally, disconnected systems can hinder real-time data tracking, reconciliation, and compliance, making the management of lease obligations even more challenging.
- Multiple ERP systems: Manufacturers often use diverse ERP systems across various plants or departments, which leads to siloed data and manual reconciliation efforts. This fragmentation complicates financial reporting and lease management, resulting in inaccuracies and delays.
- Data security risks: Without robust data security measures, sensitive lease information is vulnerable during transmission and storage. Insecure connections between ERP systems and cloud platforms, coupled with weak access controls, can expose data to unauthorized access, increasing the risk of security breaches. Compliance failures can also lead to severe legal and financial consequences.
- Real-time data flow: Timely transfer of lease data between accounting systems and ERPs is essential for accurate and up-to-date financial reporting. Manufacturers often face delays in data synchronization, which can disrupt decision-making and increase the risk of errors in financial statements.
- Complex data structures: The disparate data structures of various ERP systems can significantly complicate the synchronization of lease-related data. Ensuring that all relevant information flows seamlessly into the accounting system demands substantial effort, often leading to inconsistencies or errors. According to a KPMG survey, 43% of organizations with large, decentralized operations source their lease data from 10 to 30 or more physical locations, exacerbating this challenge. With lease contracts dispersed across multiple offices, factories, subsidiaries, and even countries, integrating this data into a unified system becomes a complex and resource-intensive task.
- Legacy system constraints: Many manufacturers still rely on outdated legacy systems, which often lack the flexibility and capability to integrate with modern lease accounting software. These legacy systems create bottlenecks, slowing down the lease management process and impeding compliance efforts.
- Disconnected lease accounting and asset management: When lease accounting, real estate, and facility management systems are not integrated, data fragmentation and inefficiencies arise. The absence of a unified system results in inconsistent asset information, manual data transfers, and misalignment between financial and operational decisions, hindering accuracy and strategic planning.
These integration challenges demand a solution that streamlines data flow, ensures security, and provides seamless ERP integration to improve operational efficiency and compliance.
How Nakisa solves technology, data security, and integration challenges for manufacturers
Nakisa Lease Accounting addresses the technology, data security, and integration challenges faced by manufacturers by offering seamless integration with leading ERP systems through the Nakisa Cloud Platform (NCP). This cloud-native platform, built with a microservices architecture, supports bidirectional integration via the Nakisa Cloud Connector (NCC), ensuring smooth integration with major ERP systems such as SAP (S/4HANA and ECC), Oracle (EBS and Fusion), and Workday. Additionally, Nakisa’s powerful APIs offer flexible integration with other ERPs and third-party systems like BlackLine, providing manufacturers with enhanced operational efficiency. Additionally, Nakisa operates through a global network of data centers, which includes multiple sites in the United States, Canada, Germany, Singapore, and the United Arab Emirates.
- Bidirectional integration: Nakisa ensures real-time, bidirectional data flow between lease accounting software and ERP systems, eliminating the need for manual data transfers or reconciliations. This seamless exchange of data between systems helps reduce errors and improves efficiency, ensuring financial data is always accurate and up to date.
- Nakisa AI Assistant: Leveraging the power of Generative AI and Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) technology, Nakisa’s conversational AI assistant provides intelligent, context-aware support. It’s trained on Nakisa’s extensive documentation library to provide accurate and relevant responses, boosting productivity by streamlining workflows. Manufacturers can ask about lease accounting topics or product functionalities, receiving precise, tailored information to enhance user experience and decision-making.
- Nakisa AI Agents: AI Agents are advanced, task-specific AI models designed to optimize complex workflows, minimize manual work, and improve operational efficiency. Unlike traditional automation tools, these agents utilize cutting-edge AI technologies to understand context, adapt to changing conditions, and perform tasks within applications based on user prompts. In their most advanced form, agentic AI can operate autonomously, making decisions, taking actions, and continuously learning to solve intricate, multi-step problems. Nakisa is developing a range of AI Agents, each tailored to its specific products and suites, identified by the "AI" in their titles. The Nakisa AI Agent is now integrated into custom dashboards within Nakisa Lease Accounting, providing enhanced functionality for dashboard creation and management by automatically generating insightful charts about your portfolio.
In Nakisa Lease Accounting, users can interact with an AI Agent to generate a real-time analytics dashboard.
- Data security: Nakisa ensures robust data security during data transmission by utilizing encrypted tunnels to securely transfer information from ERP systems to the Nakisa Cloud Platform. Once the data reaches its destination, encryption at rest guarantees its protection. With role-based access control, access control lists, and firewall rules within a virtual private cloud, Nakisa minimizes external threats. Compliance with ISO 27001, ISO 27017, SOC 1 Type II, and SOC 2 Type II standards ensures that only authorized personnel have access, with regular audits monitoring data security practices.
- Multi-ERP integration: Nakisa is designed to handle complex multi-ERP integration scenarios, making it an ideal solution for manufacturers who operate across different regions and use various ERP systems. Whether manufacturers use SAP, Oracle, or Workday, Nakisa consolidates lease data from multiple ERP systems into a single unified instance, streamlining the process and reducing administrative burden.
- Real-time data synchronization: Nakisa enables real-time synchronization between lease accounting software and ERP systems, ensuring that all lease-related financial data is consistent and accurate across the enterprise. This leads to better financial oversight and control, allowing manufacturers to keep track of lease liabilities, payments, and obligations in real-time.
- Scalability and flexibility: As manufacturing organizations grow and expand into new markets, Nakisa’s integration capabilities scale to meet the needs of larger, more complex portfolios. Whether adopting new ERP systems or expanding operations, the integration process remains smooth and seamless, ensuring that manufacturers can stay agile and compliant as they evolve.
- Unified lease accounting and asset management: Nakisa Lease Accounting integrates with Nakisa IWMS to unify lease accounting, real estate, and facility management through a single asset repository. This integrated approach enhances cross-functional collaboration, ensures alignment between financial and operational data, and provides a comprehensive solution to manage assets and leases efficiently.
Robbie Hayden
Director – Process Risk and Control at NU Skin Enterprises
Challenge 9: Lack of cross-functional collaboration in manufacturing
A key challenge faced by manufacturing organizations is the lack of cross-functional collaboration between accounting, real estate, and facility management teams. This disconnect can lead to inefficiencies, inaccurate lease data, and delays in decision-making. For manufacturers, accurate, real-time data is essential for maintaining compliance with accounting standards like IFRS 16 and ASC 842. However, while accounting teams focus on financial aspects, real estate and facility management teams handle the operational side of leases, such as space utilization, maintenance, and facilities management. Without seamless collaboration and integration, discrepancies between financial and operational data can arise, complicating lease management, reporting, and compliance. Here are the Key challenges when teams work in silos:
- Inconsistent data: Accounting teams may rely on outdated or manually collected operational data for financial reporting, leading to inaccuracies in lease calculations, payment schedules, and compliance.
- Delayed updates: Changes like lease renewals, terminations, or reconfigurations may not be communicated between departments promptly, resulting in outdated records or incorrect financial entries.
- Inefficient processes: The lack of collaboration can lead to duplicated data entry, errors, and time-consuming manual reconciliation processes, reducing efficiency and increasing compliance risks.
- Limited visibility: When financial and operational data are stored separately or not integrated, stakeholders lack a comprehensive view of lease obligations, making it harder to assess the impact of operational changes on financial reporting.
How Nakisa IWMS solves cross-functional collaboration challenges for manufacturers
Nakisa Lease Accounting (NLA), as part of Nakisa IWMS, bridges the gap between lease accounting, real estate, and facility management teams to foster cross-functional collaboration. It ensures both financial and operational data are aligned and shared seamlessly across the organization.
- Single asset repository: Nakisa IWMS integrates lease accounting, real estate, and facility management into a single asset repository. This eliminates data silos, synchronizing information in real-time and enhancing cross-functional collaboration. This seamless integration ensures data consistency, improving accuracy, efficiency, compliance, and strategic decision-making.
- Streamlined workflows: The integration removes the need for duplicate data entry, reducing errors. Changes made in the IWMS system such as lease modifications, space adjustments, or maintenance updates, are automatically reflected in the lease accounting system. This ensures that lease liabilities, right-of-use assets, and payment schedules remain accurate and up to date.
- Real-time updates: Key events, like lease renewals, terminations, and space reconfigurations, are tracked and communicated seamlessly between accounting, real estate, and facility management teams. This ensures all teams are working with the same data, reducing miscommunication and enabling faster, more accurate decisions.
- Comprehensive reporting: With Nakisa’s integrated systems, cross-functional teams gain enhanced visibility into both financial and operational data. This enables them to access real-time, comprehensive reports that reflect both the financial and operational status of each lease, improving decision-making and strategic planning across the organization.
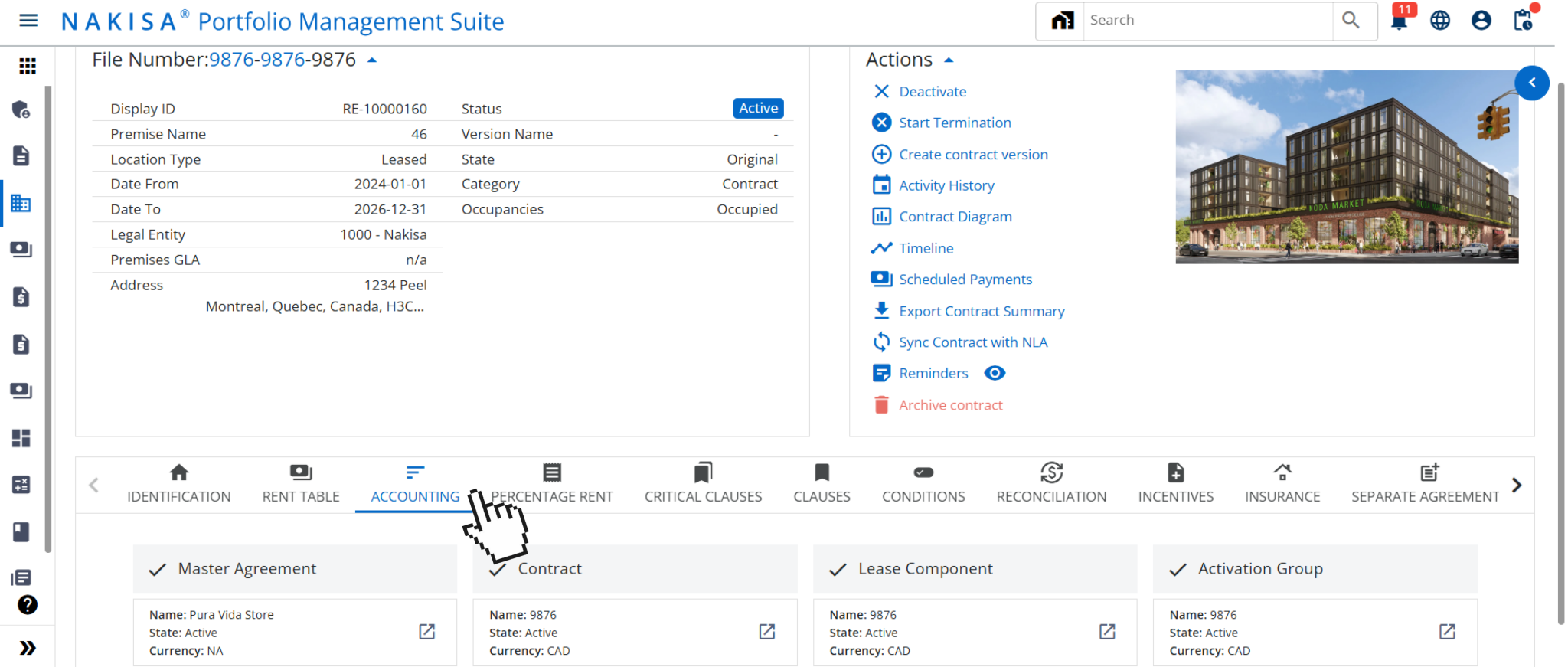
Nakisa Lease Management software seamlessly integrates with Nakisa Lease Accounting software through the Accounting tab.
Eric Cabana
Senior Real Estate Advisor at TC Transcontinental
Explore our buyer's guide, featuring an RFP scorecard designed to streamline the selection of lease accounting solutions for the manufacturing industry. With customized evaluation criteria and actionable insights, this guide supports you in making informed decisions and finding the tools that best match your organization’s specific needs.
Conclusion
For global manufacturers, managing an expansive and diverse lease portfolio presents unique challenges. With a vast array of assets across multiple regions, the complexities of handling complex lease structures, variable payment terms, and ever-evolving business requirements can be overwhelming. These challenges are compounded by the need to stay compliant with global accounting standards such as with IFRS 16, ASC 842, and local GAAP while seamlessly integrating data across ERP systems.

Nakisa Lease Accounting empowers global manufacturers such as Nestlé, 3M, Volvo, PUMA, Mondi, Grupo Gondi, UPM, KONE, Swiss Steel, Nu Skin, EMCO, Olin Corporation, and Bunge by managing complex lease structures and streamlining variable payments. The solution integrates seamlessly with existing ERP systems, enabling efficient mass operations and eliminating manual, error-prone processes across multiple regions. With Nakisa, manufacturers can confidently streamline operations, optimize lease data management, and ensure compliance with all relevant standards, no matter how complex the lease arrangements or how extensive the global operations.
We invite you to explore how Nakisa Lease Accounting can streamline your lease accounting processes and ensure full compliance with relevant standards. Schedule a personalized demo to experience how our solution can help enhance your enterprise's operational efficiency, simplify complex lease management, and support long-term success for your global manufacturing operations.